Conclusions
-
1.
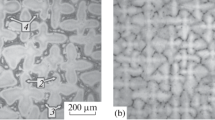
Alloys of the system Ni−Fe−Zr with an atomic fraction of zirconium not more than 0.5% solidify from the melt by a cellular mechanism, but with a content of 3–8.5% Zr solidification from the melt occurs by a dendritic mechanism.
-
2.
The crystallographic texture of Ni−Fe−Zr-alloys is characterized by orientations {100}<OVW>.
-
3.
During annealing at temperatures up to 900°C grain growth in alloys with ≤0.5% Zr does not occur.
-
4.
On alloying with zirconium there is strengthening of microcrystalline Ni−Fe-alloys which is due to refinement of the structure and the presence of Ni5Zr phase particles. The maximum microhardness (1250 N) is obtained for alloy Ni-15% Fe-8.5% Zr after annealing at 600°C. The maximum ultimate breaking strength (σf = 1000 N/mm2) occurs for alloy Ni-15% Fe-3% Zr after annealing at 900°C.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
V. V. Sosnin, A. M. Glezer, and O. M. Zhigalina, "Features of the structure and physicomechanical properties of microcrystalline alloys of the system Ni−Fe−Nb (Mo)", Metalloved. Term. Obrab. Met., No. 3, 28–33 (1992).
K. Lohberg and G. Schmidt, "Beitrag zur kornfeinenden Wirkung des Zirkons in Magnesium-legierungen", Giessereiforschung,27, No. 3, 75–82 (1975).
C. T. Ho, C. J. Cheng, and J. A. Sekhar, "Solidification microporosity in directionally solidified multicomponent Ni aluminide", Met. Trans.,22A, No. 1, 225–234 (1991).
A. M. Glezer and O. L. Utevskaya, "Development of a procedure for measuring mechanical properties of thin tape materials", in: Composite Precision Materials [in Russian], Metallugiya, Moscow (1983), pp. 78–82.
R. Elliot, Control of Eutectic Solidification [Russian translation], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1987).
A. M. Glezer and B. V. Molotilov, Ordering and Deformation of Alloys Based on Iron [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1984).
V. V. Sosnin, A. M. Glezer, and B. V. Molotilov, "Structural stability and physicomechanical properties of microcrystalline alloy sendast," in: Problems of Studying the Structure of Amorphous Metal Alloys: Proc. All-Union Sci. Conf. MiSIS, Moscow (1984), pp. 171–174.
Additional information
I. P. Bardin Institute of Ferrous Metallurgy, Moscow. Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskayq Obrabotka Metallov, No. 4, pp. 25–28, April, 1992.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhigalina, O.M., Sosnin, V.V. & Glezer, A.M. Structure and mechanical properties of microcrystalline alloys of the system Ni−Fe−Zr. Met Sci Heat Treat 34, 263–268 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00702547
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00702547