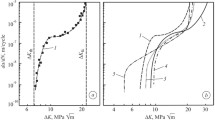
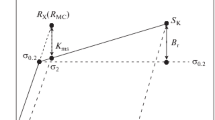
Conclusions
A correlation of quite general character evidently exists relative to the positive effect of alloying elements on the resistance of metallic alloys to fracture in a number of cases. In particular, a physical connection, is observed between the transformation temperature of the matrix phase and the prevention of various types of brittle fracture. This is related, in principle, to the nature of the change in the electronic structure of the metal produced by alloying and (in titanium alloys) to suppression of the processes of decomposition of the solid solution. The well known positive correlation between the coldbrittleness threshold and the melting point of an alloy can be considered as a degenerate case in which the phase transformation temperature and melting point coincide.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
A. P. Gulyaev, Metal Science [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1986).
L. A. Ivanova, A. I. Igolkin, and Yu. D. Khesin, "The effect of isomorphic β-stabilizing elements on the susceptibility of α-titanium alloys to corrosion cracking in aqueous chloride solutions," Metalloved. Term. Obrab. Met., No. 10, 48–51 (1988).
L. A. Ivanova, A. I. Igolkin, S. N. Petrov, and Yu. D. Khesin, "Corrosion cracking of (α+β)-titanium alloys in relation to the time-temperature parameters of thermoplastic treatment," Fiz.-Khim. Mekh. Mater., No. 1, 118–120 (1990).
L. A. Ivanova, A. I. Igolkin, and, Yu. D. Khesin, "Anisotropy of the stress-corrosion resistance of α-titanium alloys," Probl. Prochn., No. 12, 108–110 (1989).
L. A. Ivanova, A. I. Igolkin, S. S. Ushkov, and Yu. D. Khesin, "Effect of β-stabilizing elements on the corrosion cracking of α-titanium alloys in chloride solutions," Metalloved. i Tekh. Legk. Splav., VILS, Moscow (1990) pp. 104–110.
M. J. Blackburn, J. A. Feeney, and T. R. Beck, "Stress-corrosion cracking of titanium alloys," Advan. Cor. Sci. Technol.,3, 67–292 (1973).
S. G. Glazunov and V. N. Moiseev, Structural. Titanium Alloys [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1974).
V. N. Moiseev, Yu. I. Zakharov and E. V. Znamenskaya, "Prospective developments in high strength titanium alloys," in Titanium: Physical Metallurgy and Technology, Vol. 3, VILS, Moscow (1978) pp. 285–292.
L. S. Moroz, B. B. Chechulin, I. V. Polin, et al., Titanium and Its Alloys [in Russian], Sudpromgiz, Leningrad (1960).
S. Terauti, Kh. Matsumoto, T. Sugimoto, and K. Kamen, "Equilibrium phase diagram of the binary Ti-Mo system," in Titanium: Physical Metallurgy and Technology [in Russian], Vol. 2, VILS, Moscow (1978) pp. 395–408.
D. K. Chernov, in: Selected Works in Metallurgy and Metal Science [in Russian], V. D. Sadovskii, ed., Nauka, Moscow (1983).
A. P. Gulyaev "Ductile and brittle fracture of steel," Metalloved. Term. Obrab. Met., No. 7, 63–64 (1977).
G. V. Samsonov, I. F. Pryadko, and L. F. Pryadko, Localization of Electrons in Solid Bodies [in Russian], Nauka, Moscow (1976).
V. G. Glushchenko, "The nature of cold brittleness in the transition metals," Metalloved. Term. Obrab. Met., No. 4, 2–4 (1982).
A. P. Gulyaev and T. F. Volynova, "Cold brittleness of the α-, ε-, and γ-solid solutions of Fe−Mn alloys," Metalloved. Term. Obrab. Met., No. 2, 17–23 (1979).
T. D. Nakorneev, "Effect of alloying elements on the ductile-brittle transition in iron alloys," Candidate's Dissertation Technical Sciences, Tuymen' (1974).
O. P. Nazimov and A. A. Il'in, "Electronic structure, phase stability, and the properties of titanium alloys," in: Electronic Structure and Physicochemical Properties of Refractory Compounds and Alloys [in Russian], Naukova Dumka, Kiev (1980), pp. 258–263.
F. L. Lokshin, O. S. Korobov, and N. A. Bannaya, "Effects of chemical composition on the formation of the ordered 228-1 in titanium alloys," Tekhnol. Legk., Splav., No. 5, 44–48 (1973).
M. K. Grigorovich, Metallic Bonding and the Structure of Metals [in Russian], Nauka, Moscow (1988).
Additional information
TsNII "Prometei". Translated from Metallovedenie i Termichiskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 4, pp. 2–4, Aprill, 1992.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Igolkin, A.I. Effect of alloying elements on the susceptibility of metallic alloys to brittle fracture. Met Sci Heat Treat 34, 225–228 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00702538
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00702538