Conclusions
-
1.
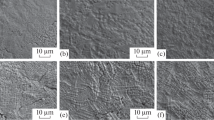
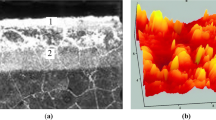
As a result of pulsed action of laser radiation on the surface of steel covered with a boron-containing covering, processes of formation of highly disperse boride phases occur in the fusion zone and cause a substantial increase of hardness of the surface.
-
2.
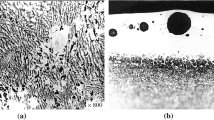
When steel is boronized with pure boron carbide, the fusion zone has a highly disperse granular structure. When chromium is contained in the boron-containing covering, the fusion zone has a ledeburite-like dendritic structure.
-
3.
The structure of the surface layer obtained by laser borochromizing has high thermal stability: after holding at 860°C and subsequent cooling in air there is no substantial decrease of hardness of the layer.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
M. A. Krishtal, A. A. Zhukov, and A. N. Kokora, Structure and Properties of Alloys Treated by Laser Radiation [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1973).
A. I. Betaneli, L. I. Danilenko, T. N. Loladze, et al., "Investigation of the possibility of additional alloying of the surface of steel R18 with the aid of a laser beam," Fiz. Khim. Obrab. Mater., No. 6, 22–26 (1972).
S. A. Isakov, V. P. Pakhadnya, and V. M. Kartoshkin, "Obtaining heat resistant layers in laser carburization of steel," Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved., Chern. Metall., No. 1, 112–115 (1985).
J. Ready, Industrial Laser Application [Russian translation], Mir, Moscow (1981).
K. Wissenbach, A. Gasser, A. Gillner, et al., "Einschmelzlegieren mit Hochleistungslasern," Laser und Optoelektron.,17, No. 4, 376–384 (1985).
V. V. Goryushin and A. V. Mart'yakova, "The effect of laser treatment on the structure and properties of steel 35," Metalloved. Term. Obrab. Met., No. 1, 53–55 (1978).
A. G. Grigor'yants and A. N. Safonov, Laser Technique and Technology: In 7 Volumes; Vol. 3: Methods of Surface Laser Treatment: University Textbook [in Russian], Vyssh. Shkola, Moscow (1987).
M. Pons, M. Caillet, and A. Galerie, "La boruration superficielle du fer par faisceau laser," Mater. et Techn., No. 2, 699–708 (1985).
H. W. Bergmann, G. Barton, and J. Betz, "Einfluss der Versuchsparameter auf die Abschreckgeschwindigkeit beim Laseroberflächenumschmelzen am Biespiel ledeburitischer Stähle," Werkstofftech., No. 14, 244–252 (1983).
Additional information
Perm Polytechnic Institute. Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 8, pp. 19–22, August, 1990.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Postnikov, V.S., Tomsinskii, V.S. & Polyakov, A.S. Structure formation in the surface layer of steel in laser borochromizing. Met Sci Heat Treat 32, 576–579 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00700708
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00700708