Conclusions
-
1.
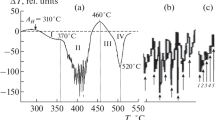
In highly pure iron (less than (C+N) 5·10−3 apm; O 0.35 apm) analysis by electron microscope did not reveal signs of martensitic transformation at cooling rates up to the maximally attainable one, viz., 570, 000°K/sec. In iron of commercial-grade purity (C, N, and O, 40 apm each) at cooling rates of more than 350,000°C/sec at step IV (at the temperature of transformation 420°C) a structure of the type of stack martensite is found.
-
2.
The temperature steps of γ→α transformation in rapid cooling depend only weakly on the degree of purity of the iron. The speed of transformation at the temperatures of each step is substantially affected by the degree of purity of the iron: the purer it is, the higher is the speed of transformation. This is due to the change of the speeds of stress relaxation and of the movement of the phase boundary in dependence on the degree of purity of the iron: these speeds increase with greater purity of the iron.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
A. Sauveur and Ch. Chih-Hung, "The gamma-alpha transformation in pure iron," Trans. ASME,84, 350–365 (1929).
H. Esser, W. Eilender, and E. Spenle, "Das Härtungsschaubild der Eisen-Kohlenstoff-Legierungen," Arch. Eisenhüttenwesen,6, No. 9, 389–393 (1933).
P. Duwez, "Effect of rate of cooling on the alpha-beta transformation in Ti and Ti-Mo alloys," J. Metals,3, No. 9, 765–771 (1951).
A. R. Entwisle, "The mechanism of phase transformation in metals," in: The Inst. of Metals Monograph and Report Series, No. 18, London (1955), pp. 315–316.
G. V. Kudryumov and M. D. Perkas, "Hardening of unalloyed carbon-free iron," Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR,111, No. 4, 818–820 (1956).
K. P. Singh and J. G. Parr, "Thermodynamic of the martensite transformation," Acta Metallurgica,9, No. 12, 1073–1074 (1961).
A. Gilbert and W. S. Owen, "Diffusionless transformation in iron-nickel, iron-chromium and iron-silicon alloys," Acta Metall.,10, No. 1, 45–54 (1962).
C. M. Wayman and C. J. Altstetter, "Martensite in zone-refined iron," Acta Metall.,10, No. 10, 992–993 (1962).
L. P. Shrivastava and J. G. Parr, "Martensite transformation in zirconium, titanium and titanium-copper alloys," Trans. ASME,224, 1295–1298 (1962).
M. J. Bibby and J. G. Parr, "The martensite transformation in pure iron," J. Iron Steel Inst.,202, No. 2, 100–104 (1964).
E. A. Wilson, "The γ→α transformation in iron and its dilute alloys," Scripta Metall.,4, 309–312 (1970).
M. Izumiyama, "Effect of cooling rate on As transformation temperature of Fe and Fe-Ni alloys," J. Jpn. Inst. Met.,34, No. 3, 286–291 (1970).
O. P. Morozov, D. A. Mirzaev, and M. M. Shteinberg, "Some regularities of transformation in iron upon rapid cooling," Fiz. Met. Metalloved.,32, No. 6, 1290–1296 (1971).
R. J. Ackert and J. G. Parr, "Massive and martensite iron-carbon alloys," J. Iron Steel Inst.,209, No. 11, 912–914 (1971).
O. P. Morozov, D. A. Mirzaev, and M. M. Shteinberg, "Polymorphic gamma→alpha transformation in highly pure iron," Fiz. Met. Metalloved.,34, No. 4, 795–800 (1972).
O. P. Morozov, D. A. Mirzaev, and M. M. Shteinberg, "Phase γ→α transformation in very pure iron," in: Problems of the Production and Processing of Steel, Issue 118, Chelyabinskii Politekkhnicheskii Institut, Chelyabinsk (1973), pp. 120–125.
M. M. Shteinberg, O. P. Morozov, Yu. D. Koryagin, et al.,: "Special features of the margensite transformation of iron base alloys," in: Problems of Production and Processing of Steel, Issue 118, Chelyabinskii Politekhnicheskii Institut, Chelyabinsk (1973), pp. 146–160.
A. P. Gulyaev and M. A. Guzovskaya, "Martensite transformation in iron," Metalloved. Term. Obrab. Met., No. 6, 2–5 (1977).
E. A. Wilson, "The γ→α transformation in iron," Scripta Metall.,12, No. 11, 961–968 (1978).
D. A. Mirzaev and V. G. Ul'yanov, "Effect of rapid cooling on polymorphic transformations in pure metals," Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Met., No. 3, 103–109 (1982).
D. A. Mirzaev, V. M. Schastlivtsev, and S. E. Karzunov, "Martensitic points of alloys Fe-C," Fiz. Met. Metalloved.,63, No. 4, 764–767 (1987).
E. A. Wilson, "γ→α transformation in Fe, Fe-Ni and Fe-Cr alloys," Metal Sci.,18, 471–484 (1984).
F. Duflos and B. Cantor, "The microstructure and kinetics of martensite transformations in splat-quenched Fe and Fe-Ni alloys," Acta Metallurgica,30, No. 2, 323–342 (1982).
D. S. Kamenetskaya, I. B. Piletskaya, and V. I. Shiryaev, "Martensite transformation in pure iron," Fiz. Met. Metalloved.,27, No. 5, 842–848 (1969).
V. I. Shiryaev, and V. D. Pautov, "Properties of iron purified by electron-beam zone melting," Fiz. Met. Metalloved.,20, No. 4, 566–569 (1965).
V. I. Shiryaev, V. D. Pautov, and Yu. M. Korobochkin, "Some special features of electronbeam zone refining of metals," Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Met., No. 1, 73–79 (1966).
V. I. Shiryaev, D. S. Kamenetskaya, I. B. Piletskaya, and V. V. Gladilin, "Properties of highly pure iron," Metalloved. Term. Obrab. Met., No. 12, 2–8 (1974).
N. A. Nedumov and V. K. Grigorovich, "Thermal effects of transformations of metals in semiconductors in the solid and the liquid states," in: The Mechanism and Kinetics of Crystallization [in Russian], Nauka i Tekhnika, Minsk (1964), pp. 297–309.
D. S. Kamenetskaya, I. B. Piletskaya, and V. I. Shiryaev, "Stress relaxation in highly pure iron," Fiz. Met. Metalloved.,36, No. 3, 605–609 (1973).
D. S. Kamenetskaya, I. B. Piletskaya, and V. I. Shriyaev, Highly Pure Iron [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1978).
D. S. Kamenetskaya, O. P. Maksimova, and V. I. Shiryaev, "Special features of martensite transformation in highly pure iron-nickel alloys," Fiz. Met. Metalloved.,55, No. 5, 965–972 (1983).
J. F. Breedis, and L. Kaufman, "Formation of HCP and BCC phases in austenitic iron alloys," Metall. Trans.,2, September, 2359–2371 (1971).
L. Kaufman and H. Bernstein, Computer Assisted Calculation of Phase Diagrams [Russian translation], Mir, Moscow (1972).
D. S. Kamenetskaya, M. P. Usikov, and V. I. Shiryaev, "Special features of phase transformations in highly pure metals and alloys," Metalloved. Term. Obrab. Met., No. 7, 9–18 (1986).
Additional information
I. P. Bardin Central Research Institute of Ferrous Metallurgy. Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 7, pp. 8–13, July, 1990.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamenetskaya, D.S., Usikov, M.P. & Shiryaev, V.I. Structure of highly pure iron after γ→α transformation at at high cooling rates. Met Sci Heat Treat 32, 476–482 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00700313
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00700313