Conlcusion
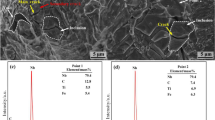
In high-temperature deformation of steel slippage is observed along the inclusion-matrix interphase boundaries for different types of nonmetallic inclusions. Slippage along inclusion-matrix boundaries causes an increase in crack resistance of the steel at high temperatures.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
O. A. Kaibyshev and R. Z. Valiev, Grain Boundaries and the Properties of Metals [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1987).
G. I. Bel'chenko and S. I. Gubenko, Nonmetallic Inclusions and the Quality of Steel [in Russian], Tekhnika, Kiev (1980).
M. G. Lozinskii, The Structure and Properties of Metals and Alloys at High Temperatures [in Russian], Metallurgizdat, Moscow (1963).
T. I. Litvinova, V. P. Pirozhkova, and A. K. Petrov, The Petrography of Nonmetallic Inclusions [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1972).
S. I. Gubenko and A. M. Galkin, "The question of the nature of red-shortness of steel," Metalloved. Term. Obrab. Met., No. 10, 11–15 (1984).
Additional information
Dnepropetrovsk Metallurgical Institute. Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 11, pp. 2–5, November, 1990.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gubenko, S.I. Slippage along nonmetallic inclusion-matrix of the steel boundaries. Met Sci Heat Treat 32, 807–811 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00700056
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00700056