Summary
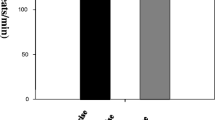
A volumetric microrespirometer was used to investigate chages in the tissue respiration of the adrenals, thyroid and pituitary of rats after a single exhausting physical exercise. The animals were made to run on a treadmill for 90 min, that is, until they showed signs of fatigue.
Oxygen uptake increased in the adrenals hy 39.1% but decreased in the thyroid by 51.9% and in the pituitary by 37.4%. It should be emphasized that the changes were statistically highly significant.
The authors suppose that increased adrenal O2 uptake may have been due to the stimulating influence of ACTH on the respiration processes in the cortex and intensification of oxidative processes in the medulla, and also increased blood supply in the entire organ during physical work.
Diminished consumption of oxygen by the thyroid may have been caused by the inhibitory influence of factors connected with stress (the inhibitory influence of ACTH and corticosteroids, effort sympathicotonia, and increased body temperature).
The decreased respiration of the pituitary is difficult to interpret but may have been caused by diminished blood supply and perhaps also an overheating of the organism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blair-West, J. R., J. P. Coghlan, D. A. Denton, J. R. Goding, J. M. Munro, R. E. Peterson, andM. Wintour: Humoral stimulation of adrenal cortical secretion. J. clin. Invest.41, 1606–1627 (1962).
Blok, W., M. Glintecka, andW. Wanic: Fatigue and adrenocortical functioning (pol.). Przegl. lek.23, 757 (1967).
Brown-Grant, K.: The effect of ACTH and adrenal steroids on thyroid activity, with observations on the adrenal-thyroid relationship. J. Physiol. (Lond.)131, 58–69 (1956).
, andJ. G. Gibson: The effect of exogenous and endogenous adrenaline on the uptake of radio-iodine by the thyroid gland of the rabbit. J. Physiol. (Lond.)131, 85–101 (1956).
, andG. Pethes: The response of the thyroid gland of the guinea-pig to stress. J. Physiol. (Lond.)151, 40–50 (1960).
,G. W. Harris, andS. Reichlin: The effect of emotional and physical stress on thyroid activity in the rabbit. J. Physiol. (Lond.)126, 29–40 (1954).
,G. W. Harris, andS. Reichlin The influence of the adrenal cortex on thyroid activity in the rabbit. J. Physiol. (Lond.)126, 41–51 (1954).
Cornil, A., A.De Coster, G. Copinschi, andJ. R. M. Franckson: Effect of muscular exercise on the plasma level of cortisol in man. Acta endocr. (Kbh.)48, 163–168 (1965).
Covasneanu, Z., A. Stahcu etN. Sterescu: Variations saisonnières de la résponse de la thyroide à l'effort physique (recherches à l'aide de l'iode et du phosphore radioactifs). Stud. Cercat. Fiziol.6, 335–341 (1961).
Derevenco, P., V. Derevenco, Z. Uray etT. Holan: L'irrigation de certains organs endocrines et non endocrines après l'effort physique et sous l'effet pharmacologique. Rev. Roum. Physiol.4, 195–203 (1967).
Eränkö, O., M. J. Karvonen, andL. Räisänen: Long-term effects of muscular work on the adrenal medulla of the rat. Acta endocr. (Kbh.)39, 285–287 (1962).
Erez, V. P.: The influence of prolonged physical exercise on the function of the hypophyseo-adrenocortical system in elderly subjects (russ.). Ter. Arkh.3, 15–18 (1964).
Gollnick, P. D., P. J. Struck, andT. P. Bogyo: Lactic dehydrogenase activities of rat heart and skeletal muscle after exercise and training. J. appl. Physiol.22, 623–627 (1967).
Grodziński, W., and R. Z.Klekowski: Methods of ecological bioenergetics (in preparation).
Keidel, R.: Kurzgefaßtes Lehrbuch der Physiologie. Stuttgart: Thieme 1967.
Kleinzeller, A.: Manometrische Methoden und ihre Anwendung in der Biologie und Biochemie. Jena: Fischer 1965.
Kovács, E., H. H. Mazareau, andG. Jojárt: The effect of ACTH on the catalase activity on the adrenal gland in in vivo experiments. Preliminary communication. Path: et Microbiol. (Basel)30, 12–14 (1967).
Kramer, R. J., andL. A. Sapirstein: Blood flow to the adrenal cortex and medulla. Endocrinology81, 403–405 (1967).
Michailov, Yn. M.: The effect of certain corticosteroids and ACTH on the functional activity of the thyroid gland under experimental and clinical conditions (russ.). Probl. Éndokr. Gormonoter.12, 5–8 (1966).
Namysłowski, L.: Adaptation of adrenals to graded exercises in trained and untrained rats (pol.). Endokr. pol.9, 223–242 (1958).
Noack, H., u.P. Schwartze: Veränderungen von Schilddrüse, Nebenniere und Hypophyse bei kastrierten und unkastrierten erwachsenen Ratten im Schwimmversuch. Endokrinologie37, 119–133 (1959).
Ottowicz, J., K. Nazar, andA. Wołowska: Effect of physical effort on the content of corticosteron and ascorbic acid in the adrenals in rats (pol.). Wych. Fiz. Sport11, 119–126 (1967).
Palkovič, M., andL. Mancho: The effect of adrenocortiootropic (ACTH) on the metabolism of the adrenal glands of the rat. Physiol. bohemoslov.13, 529–533 (1964).
Palumbo, R., eE. Rottini: Osservazione sulla funzionalita tireidea dopo attivà sportiva. Med. dello Sport20, 19–23 (1967).
Plas, F.: Standardisation des tests d'appitude physique. Méd. Educ. phys. Sport.39, 11–29 (1965).
Romanowski, W., andL. Lubańska-Tomaszewska: The mechanism of electro-pherographic changes in blood serum proteins under the influence of physical training. Acta physiol. pol.13, 639–649 (1962).
, andW. Strazyński: Effect of exercise on tissue respiration of the brain, skeletal muscle, heart, liver, kidneys, and spleen. Int. Z. angew. Physiol.25, 329–338 (1968).
Selye, H.: The physiology and pathology of exposure to stress. Montreal: Acta, Inc. Medical Publishers 1950.
Sterescu, N., Z. Covásneanu, andA. Stancu: Peculiar features of thyroid inhibition during physical work. Rev. Sci. méd.5, 235–239 (1960).
etA. Stancu: Étude comparative des modifications de la fixation du radio-phosphore (P32) et du radio-iode (J131) dans la glande thyroide des cobayes soumi a l'effort. Stud. Cercat. Fiziol.5, 759–766 (1960).
: Influence de l'effort physique aigu sur l'état fonctionnel de la thyroid du rat (études effectuées à l'aide de l'iode radio-actif J131). Stud. Cercat. Fiziol.5, 509–514 (1960).
, E. Gabrielescu et A. Bordeianu: Influence de léffort physique sur le développement du goitre expérimental par antithyroidiens de synthèse. Stud. Cercat. Fiziol.5, 247–254 (1960).
Suzuki, T., K. Otsuka, H. Matsui, S. Ohukuzi, K. Sakai, andY. Harada: Effect of muscular exercise on adrenal 17-hydroxycorticosteroid secretion in the dog. Endocrinology80, 1148–1151 (1967).
Vennig, E. H., andV. Kazmin: Excretion of urinary corticoids and 17-keto-steroids in the normal individual. Endocrinology39, 131–139 (1946).
Williams, R. H.: Textbook of Endocrinology. Philadelphia and London: Saunders 1962.
Wojcieszak, I., I. Malarecki, B. Obuchowicz, andM. Wilk: The effect of training under hypoxic conditions on the respiratory gase exchange, morphological and enzymatic changes in blood and thyroid gland activity (pol.). Wych. Fiz. Sport.11, 81–93 (1967).
Yates, F. E., R. Kirschman, andB. Olshen: Analysis of adenohypophysial blood flow in the rat by radioisotope washout: estimate of the vasomotor activity of vasopressin in the anterior pituitary. Endocrinology79, 341–351 (1966).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Strazyński, W., Romanowski, W. Effect of physical exercise on tissue respiration of endocrine glands. Int. Z. Angew. Physiol. Einschl. Arbeitsphysiol. 26, 290–297 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00698305
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00698305