Conclusions
-
1.
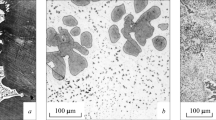
The addition of a surface-active element (magnesium) increases the dispersity and uniformity of the structure, reducing the average grain size of the α-solid solution and the inclusions of excess plases in quenched beryllium bronzes.
-
2.
Microalloying of beryllium bronzes B2 and BNT1.9 with magnesium substantially improves their strength characteristics (elastic limit, relaxation resistance, cyclic strength) as the result of suppression of the discontinuous decomposition mechanism and the uniform strengthening of both the bulk and grain boundary areas. The best strength characteristics of beryllium bronzes were attained with 0.1$ Mg.
-
3.
The newly developed compositions, alloyed with Mg, are designated BNT1.9Mg and B2Mg. The optimal heat treatment for these alloys is quenching from 770°C and aging at 320°C for 6h.
-
4.
Commercial trials of the new beryllium bronzes showed that elastic elements of these bronzes have better combinations of basic properties than those of the standard compositions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
A. G. Rakhshtadt, Spring Alloys [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1965).
Hiroshi Itsu, Takashi Agatsuma, and Kimo Hashidzumi, Mitsubishi Denki Gaio,41, No. 6 (1967).
A. I. Chipizhenko, Byull. TsIIN MTsM SSSR,7 (84) (1957).
A. I. Chipizhenko, in: Promising Developments in Elastic Sensing Elements [in Russian], TsIIN Élektrotekhnicheskoi Promyshlennosti i Priborostroeniya (1961).
A. G. Rakhshtadt and A. M. Grishin, Stal' No. 9 (1969).
G. S. Ionychev, Zh. P. Pastukhova, A. G. Rakhshtadt, and N. F. Komissarova, Izv. Vuzov., Mashinostroenie, No. 1 (1968).
S. N. Zadumkin, Zh. Neorgan. Khim., No. 8 (1960).
A. G. Rakhshtadt and M. A. Shtremel', Zavod. Lab., No. 6 (1960).
V. I. Arkharov, Trudy Inst. Fiz. Metal., UFAN, No. 19 (1958).
W. Bonfeld, Trans. Met. Soc. AIME,239, No. 1 (1967).
P. Wilkes, Acta Met.,16, (1968).
G. Newkirk, Aging of Alloys [Russian translation], Metallurgizdat, Moscow (1962).
D. Turnbull, Acta Met.,3 (1955).
Additional information
Bauman Moscow Higher Technical School. Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 2, pp. 19–24, February, 1970.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tkhagapsoev, K.G., Rakhshtadt, A.G., Pastukhova, Z.P. et al. Structure and properties of beryllium bronze microalloyed with magnesium. Met Sci Heat Treat 12, 106–111 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00695887
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00695887