Abstract
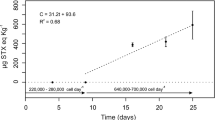
Two different phytoplankton sampling methods (bottle and net sampling) were used to evaluate the concentration of toxicDinophysis species in seawater and their correlation to mussel toxicity, assessed by mouse bioassay.Dinophysis concentration in net samples revealed the higher correlation to mussel toxicity (r=0.75,p<0.01). Net sampling therefore seems more suitable for the detection of low abundance species likeDinophysis characterised by vertical aggregations at different depths in the water column.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belin C, Berthome JP (1991) Reply: le reseau francais de suivi du phytoplancton. In Frémy JM (ed.), Proceedings of Symposium on Marine Biotoxins, CNEVA, Paris: 189–194.
Beers JR (1978) Pump sampling. In Sournia A (ed.), Phytoplankton Manual, UNESCO, Paris: 41–49.
Della Loggia R, Cabrini M, Del Negro P, Honsell G, Tubaro A (1993) Relationship betweenDinophysis spp. in seawater and DSP toxins in mussels in the Northern Adriatic Sea. In Smayda TJ, Shimizu Y (eds), Toxic Phytoplankton Blooms in the Sea. Elsevier Science Publishers, New York: 483–488.
Hald B, Bjergskov T, Emsholm H (1991) Monitoring and analytical programmes on phycotoxins in Denmark. In Frémy JM (ed.), Proceedings of Symposium on Marine Biotoxins, CNEVA, Paris: 181–187.
ICES (1992) Effects of harmful algal blooms on mariculture and marine fisheries. ICES Cooperative Research Report no 181 Copenhagen, 38 pp.
Lassus P, Proniewski F, Pigeon C, Veret L, Le Déan L, Bardouil M, Truquet P (1990) The vertical migrations ofDinophysis acuminata in an outdoor tank at Antifer (Normandy, France). Aquat. Living Resour. 3: 143–145.
Lund JWG, Kipling C, Le Cren ED (1958) The inverted microscope method of estimating algal numbers, and the statistical basis of estimation by counting. Hydrobiologia 11: 143–170.
Ministero della Sanità (1990) Gazzetta Ufficiale della Repubblica Italiana, Serie generale 218: 8–13.
Tangen K (1978) Nets. In Sournia A (ed.), Phytoplankton Manual, UNESCO, Paris: 50–58.
Tubaro A, Sosa S, Bussani D, Sidari L, Honsell G, Della Loggia R (1995) Diarrhoeic toxicity induction in mussels of the Gulf of Trieste. In Lassus P, Erard E, Gentien P, Marcaillou C (eds), Harmful Marine Algal Blooms, Lavoisier Science Publishers, Paris: 249–254.
Yasumoto T, Oshima Y, Yamaguchi M (1978) Occurence of a new type of shellfish poisoning in the Tohoku district. Bull. Jap. Soc. Sci. Fish. 44: 1249–1255.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sidari, L., Nichetto, P., Cok, S. et al. Phytoplankton detection and DSP toxicity: methodological considerations. J Appl Phycol 7, 163–166 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00693063
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00693063