Summary
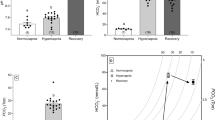
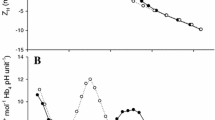
Carbon dioxide excreted across fish gills is hydrated catalytically to form HCO −3 and H+ ions in water near the gill surface. We tested the possibility that CO2 excretion is functionally linked to ammonia excretion through chemical reactions in the gill-water boundary layer. A bloodperfused trout head preparation was utilized in which the convective and diffusive components of branchial gas transfer were controlled. Pre-incubation of blood perfusate with the carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, acetazolamide, reduced both carbon dioxide and ammonia excretion in the blood-perfused preparation. Increasing the buffering capacity of inspired ventilatory water significantly reduced ammonia excretion, but carbon dioxide excretion was unaffected. Each of these experimental treatments significantly reduced the acidification of ventilatory water flowing over the gills. It is proposed that the catalysed conversion of excreted CO2 to form HCO −3 and H+ ions provides a continual supply of H+ ions need for the removal of NH3 as NH +4 . We suggest, therefore, that acidification of boundary layer water by CO2 enhances blood-to-water NH3 diffusion gradients and facilitates ammonia excretion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bornancin M, Isaia J, Masoni A (1985) A re-examination of the technique of isolated, perfused trout head preparation. Comp Biochem Physiol 81A:35–41
Cameron JN, Davis JC (1970) Gas exchange in rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) with varying blood oxygen capacity. J Fish Res Bd Can 27:1069–1085
Cameron JN, Heisler N (1983) Studies of ammonia in the rainbow trout: physico-chemical parameters, acid-base behavior, and respiratory clearance. J Exp Biol 105:107–125
Davie PS, Daxboeck C (1983) Modification of a piston-type perfusion pump for delivery of low flow rates. Experientia 39:433–434
Daxboeck C, Davies PS, Perry SF, Randall DJ (1982) Oxygen uptake in a spontaneously ventilating blood-perfused trout preparation. J Exp Biol 101:35–45
Evans DH (1977) Further evidence for Na/NH4 exchange in marine teleost fish. J Exp Biol 70:213–220
Girard JP, Payan P (1980) Ion exchanges through respiratory and chloride cells in freshwater- and seawater-adapted teleosteans. Am J Physiol 238:R260-R268
Iwama G, Boutilier RG, Heming TA, Randall DJ, Mazeaud M (1987) The effects of altering gill water flow on gas transfer in rainbow trout. Can J Zool 65:2466–2470
Johansen K, Maloiy GMO, Lykkeboe G (1975) A fish in extreme alkalinity. Resp Physiol 24:159–162
Kiceniuk JW, Jones DR (1977) The oxygen transport system in trout (Salmo gairdneri) during sustained exercise. J Exp Biol 69:247–260
Kirschner LB, Greenwald L, Kerstetter TH (1973) Effect of amiloride on sodium transport across body surfaces of freshwater animals. Am J Physiol 224:832–837
Kun E, Kearney EB (1971) Ammonia. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Methods of enzymatic analysis, vol 4. Academic Press, New York, pp 1802–1806
Maetz J (1973) Na+/NH +4 , Na+/H+ exchanges and NH3 movement across the gill ofCarassius auratus. J Exp Biol 58:255–275
Maetz J, Garcia Romeu F (1964) The mechanism of sodium and chloride uptake across the gills of a freshwater fish,Carassius auratus II. Evidence for NH +4 /Na+ and HCO −3 /Cl− exchanges. J Gen Physiol 47:1209–1227
Maren TH (1977) Use of inhibitors in physiological studies of carbonic anhydrase. Am J Physiol 232:F291-F297
Maren TH, Swenson ER (1980) A comparative study of the kinetics of the Bohr effect in vertebrates. J Physiol 303:535–547
McDonald DG, Wood CM (1981) Branchial and renal acid and ion fluxes in the rainbow trout at low environmental pH. J Exp Biol 93:101–118
Payan P (1978) A study of the Na+/NH +4 exchange across the gill of the perfused head of trout (Salmo gairdneri). J Comp Physiol 124:181–188
Payan P, Matty AJ (1975) The characteristics of ammonia excretion by a perfused isolated head of trout (Salmo gairdneri): effect of temperature and CO2-free ringer. J Comp Physiol 96:167–184
Perry SF, Wood SF (1985) Kinetics of branchial calcium uptake in the rainbow trout: effects of acclimation to various external calcium levels. J Exp Biol 116:411–433
Perry SF, Davie PS, Daxboeck C, Randall DJ (1982) A comparison of CO2 excretion in a spontaneously ventilating bloodperfused trout preparation and saline-perfused gill preparations: contribution of the branchial epithelium and red blood cell. J Exp Biol 101:47–60
Perry SF, Davie PS, Daxboeck C, Ellis AG, Smith DG (1984a) Perfusion methods for the study of gill physiology. In: Hoar WS, Randall DJ (eds) Fish physiology, vol XB. Academic Press, New York, pp 325–388
Perry SF, Lauren DJ, Booth CE (1984b) Absence of the branchial edema in perfused heads of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). J Exp Zool 231:441–445
Perry SF, Payan P, Girard JP (1984c) Adrenergic control of branchial chloride transport in the isolated perfused head of the freshwater trout (Salmo gairdneri). J Comp Physiol B 154:269–274
Perry SF, Booth CE, McDonald DG (1985a) Isolated perfused head of rainbow trout I. Gas transfer, acid-base balance, and haemodynamics. Am J Physiol 249:R246-R254
Perry SF, Booth CE, McDonald DG (1985b) Isolated perufused head of rainbow trout II. Ionic fluxes. Am J Physiol 249:R255-R261
Piiper J, Scheid P, Perry SF, Hughes GM (1986) Effective and morphometric oxygen-diffusing capacity of the gills of the elasmobranchScyliorhinus stellaris. J Exp Biol 123:27–41
Potts WTW (1984) Transepithelial potentials in fish gills. In: Hoar WS, Randall DJ (eds) Fish physiology, vol XB. Academic Press, New York, pp 105–128
Rahim S, Delaunoy JP, Laurent P (1988) Identification and immunocytochemical localization of two different carbonic anhydrase isoenzymes in teleostean fish erythrocyte and gill epithelia. Histochemistry 89:451–459
Soivio AK, Westman K, Nyholm K (1972) Improved method of dorsal aorta catheterization: haematological effects followed for three weeks in rainbow trout. Finn Fish Res 1:11–21
Swenson ER, Maren TH (1987) Roles of gill and red cell carbonic anhydrase in elasmobranch acid-base regulation and CO2 exchange. Am J Physiol 253:R450-R458
Tucker VA (1967) Method for oxygen content and dissociation curves on microliter blood samples. J Appl Physiol 23:410–414
Vermette MG, Perry SF (1987) The effects of prolonged epinephrine infusion on the physiology of the rainbow trout,Salmo gairdneri II. branchial solute fluxes. J Exp Biol 128:255–267
Wolf K (1963) Physiological salines for freshwater teleosts. Prog Fish Cult 25:135–140
Woodward JJ (1982) Plasma catecholamines in resting trout,Salmo gairdneri Richardson, by high pressure liquid chromatography. J Exp Biol 21:429–432
Wright PA, Wood CM (1985) An analysis of branchial ammonia excretion in the freshwater rainbow trout: effects of environmental pH change and sodium uptake blockade. J Exp Biol 114:329–353
Wright PA, Heming TA, Randall D (1986) Downstream pH changes in water flowing over the gills of rainbow trout. J Exp Biol 126:499–512
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wright, P.A., Randall, D.J. & Perry, S.F. Fish gill water boundary layer: a site of linkage between carbon dioxide and ammonia excretion. J Comp Physiol B 158, 627–635 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00693000
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00693000