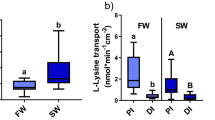
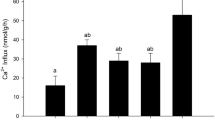
Summary
Simultaneous measurements of net ion and water fluxes were made in the stripped intestine of the seawater eel, and the relationship between Na+, K+, Cl− and water transport were examined in the presence of mucosal KCl and serosal NaCl Ringer (standard condition). When Cl− was removed from both sides of the intestine, net K+ flux from mucosa to serosa was reduced, accompanied by complete blockage of water absorption. Since it has been shown that net Cl− and water fluxes depend on K+ transport under the standard condition (Ando 1983), the interdependence of K+ and Cl− transport suggests the existence of a coupled KCl transport system, while the parallelism between the net Cl− and water fluxes suggests that water absorption is linked to the coupled KCl transport. The coupled KCl and water transport were inhibited by treatment with ouabain or with Na+-free Ringer solutions, suggesting the existence of a Na+-dependent KCl transport system and linkage of water absorption to the coupled Na+−K+−Cl− transport. Since ouabain blocked the active Na+−K+−Cl− transport almost completely, the permeability coefficients for K+ and Na+ through the paracellular shunt pathway were estimated as PK=0.076 and PNa=0.058 cm/h, and PCl was calculated as 0.005 cm/h. Although Na+-independent K+ and Cltt- fluxes were observed again in the present study, these fluxes were not inhibited by CN−, ouabain or diuretics, and evoked even after blocking the Na+−K+−Cl− transport completely with ouabain. These results indicate that the Na+-independent K+ and Cl− fluxes are distinct from the active Na+−K+−Cl− transport and are not themselves active.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ando M (1975) Intestinal water transport and chloride pump in relation to sea-water adaptation of the eel,Anguilla japonica. Comp Biochem Physiol 52A:229–233
Ando M (1980) Chloride-dependent sodium and water transport in the seawater eel intestine. J Comp Physiol 138:87–91
Ando M (1981) Effects of ouabain on chloride movements across the seawater eel intestine. J Comp Physiol 145:73–79
Ando M (1983) Potassium-dependent chloride and water transport across the seawater eel intestine. J Membr Biol 73:125–130
Ando M, Kobayashi M (1978) Effects of stripping off the outer layers of the eel intestine on salt and water transport. Comp Biochem Physiol 61A:497–501
Bakker-Grunwald T (1981) Hormone-induced diuretic-sensitive potassium transport in the turkey erythrocytes is anion dependent. Biochim Biophys Acta 641:427–431
Diamond JM (1962) The mechanism of solute transport by the gall-bladder. J Physiol 161:474–502
Dunham PB, Stewart GW, Ellory JC (1980) Chloride-activated passive potassium transport in human erythrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:1711–1715
Field M, Karnaky KJ Jr, Smith PL, Bolton JE, Kinter WB (1978) Ion transport across the isolated intestinal mucosa of the winter flounder,Pseudopleuronectes americanus. I. Functional and structural properties of cellular and paracellular pathways for Na and Cl. J Membr Biol 41:265–293
Frizzell RA, Schultz SG (1972) Ionic conductances of extracellular shunt pathway in rabbit ileum. Influence of shunt on transmural sodium transport and electrical potential differences. J Gen Physiol 59:318–346
Geck P, Pietrzyk C, Burckhardt B-C, Pfeiffer B, Heinz E (1980) electrically silent cotransport of Na+, K+ and Cl− in Ehrlich cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 600:432–447
Greger R, Schlatter E (1981) Presence of luminal K+, a prerequisite for active NaCl transport in the cortical thick ascending limb of Henle's loop of rabbit kidney. Pflügers Arch 392:92–94
Haas M, Schmidt WF III, McManus TJ (1982) Catecholaminestimulated ion transport in duck red cells. Gradient effects in electrically neutral Na+K+2Cl co-transport. J Gen Physiol 80:125–147
Holtug K, Skadhauge E (1982) NaCl transport across hen colon. Dependence on electro-chemical driving force. Pflügers Arch 394:222–225
House CR (1974) Water transport in cells and tissues. Edward Arnold, London
Musch MW, Orellana SA, Kimberg LS, Field M, Halm DR, Krasny EJ Jr, Frizzell RA (1982) Na+−K+−Cl− cotransport in the intestine of a marine teleost. Nature 300:351–353
O'Donnell MJ, Maddrell SHP (1983) Paracellular and transcellular routes for water and solute movements across insect epithelia. J Exp Biol 106:231–253
Oide M, Utida S (1967) Changes in water and ion transport in isolated intestine of the eel during salt adaptation and migration. Mar Biol 1:102–106
Palfrey HC, Rao MC (1983) Na/K/Cl co-transport and its regulation. J Exp Biol 106:43–54
Skadhauge E (1974) Coupling of transmural flows of NaCl and water in the intestine of the eel (Anguilla anguilla). J Exp Biol 60:535–546
Smith HW (1930) The absorption and excretion of water and salts by marine teleosts. Am J Physiol 93:480–505
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ando, M. Relationship between coupled Na+−K+−Cl− transport and water absorption across the seawater eel intestine. J Comp Physiol B 155, 311–317 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00687473
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00687473