Summary
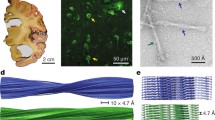
The ultrastructure of neurofibrillary tangles of Zlzheimer's disease was analyzed by computerized digital processing of electron micrographs. Processing of the electron micrographs consists of four steps: digitizing the electron micrograph, Fourier transformation, noise filtering and inverse Fourier transformation and Laplacian operation. In the present study, we have confirmed that neurofibrillary tangles are composed of a pair of helical filaments (PHF), which appear characteristically as an unbranched rigid structure. The periodicity of PHF is 78nm on the diffractogram. The dimensions of PHF obtained by our analysis, although basically similar to those described earlier by other investigators using conventional techniques, more precisely defines its structural conformation. We have also demonstrated that the spatial relationship of two filaments appears symmetrical after two-way tilting of the specimen about the axis of rotation. Our observations emphasize the importance of digital image processing as an effective tool for structural analytical research in biology and medicine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderton BH, Breinburg D, Downes MJ, Green PJ, Tomlinson BE, Ulrich J, Wood JN, Kahn J (1982) Monoclonal antibodies show that neurofibrillary tangles and neurofilaments share antigenic determinants. Nature 298:84–86
Baba N, Naka M, Muranaka Y, Nakamura S, Kino I, Kanaya K (1984) Computer-aided stereographic repressertation of an object reconstructed from micrographs of serial thin sections. Micron Microsc Acta 15:221–226
Baker TS (1981) Image processing of biological specimens: a bibliography. In: Griffith JD (ed) Electron microscopy in biology, vol 1. John Wiley and Sons, New York, pp 189–290
Blessed G, Tomlinson BE, Roth M (1968) The association between qualitative measures of dementia and of senile changes in the cerebral grey matter of elderly subject. Br J Psychiatry 114:797–811
Dahl D, Selkoe DJ, Pero R, Bignami A (1982) Immunostaining of neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer's senile dementia with a neurofilament antiserum. J Neurol Sci 2:113–119
Gambetti P, Shecket G, Ghetti B, Hirano A, Dahl D (1983) Neurofibrillary changes in the human brain. An immunocytochemical study with a neurofilament antiserum. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 42:69–79
Grundke-Iqbal I, Johnson AB, Wisniewski HM, Terry RD, Iqbal K (1979) Evidence that Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles originate from neurotubules. Lancet I:578–580
Hirano A, Dembitzer HM, Kurland LT, Zimmerman HM (1968) The fine structure of some intraganglionic alterations. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 27:167–182
Ihara Y, Abraham C, Selkoe DJ (1983) Specific recognition by antibodies of paired helical filaments in Alzheimer's disease. Nature 304:727–730
Ishii T, Haga S, Tokutake S (1979) Presence of neurofilament protein in Alzheimer's neurofibrillary tangles (ANT)—an immunofluorescent study. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 48:105–113
Kanaya K, Baba N, Shino M, Takamiya K, Oikawa T (1982) Digital processing of lattice image from a diffraction spot selected in diffractogram of electron micrograph. Micron 13:205–219
Kanaya K, Baba N, Shinohara C, Osumi M (1983) A digital processing method for the structural analysis of lttice images of crystalloids obtained by electron microscopy. Micron Microsc Acta 14:233–247
Kanaya K, Baba N, Shinohara C (1984) A digital Fourier harmonic superposition method for the structural analysis of human tooth enamel obtained by electron microscopy. Micron Microsc Acta 15:17–35
Kanaya K, Baba N, Kitagawa Y, Mukai M (1985) The digital structural analysis of human alveolar soft part sarcoma obtained by electron microscopy. Micron Microsc Acta 16:17–32
Kidd M (1963) Paired helical filaments in electron microscopy in Alzheimer's disease. Nature 197:192–193
Klug A, Berger JR (1964) An optical method for the analysis of periodicities in electron micrographs and some observations on the mechanism of negative staining. J Mol Biol 10:565–569
Klug A, De Rosier DJ (1966) Optical filtering of electron micrographs: reconstruction of one-side image. Nature 212:29–32
Klug A, Crick FHC, Wyckoff HW (1958) Diffraction by helical structures. Acta Cryst 11:199–213
Mori H, Tomonaga M, Baba N, Kanaya K (1988) The structure analysis of Hirano bodies by digital processing on electron micrographs. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) (in press)
Mukai M, Torikata C, Iri H, Mikata A, Sakamoto T, Hanaoka H, Shinohara C, Baba N, Kanaya K, Kageyama K (1984) Alveolar soft sarcoma, an elaboration of a threedimensional configuration of the crystalloids by digital image processing. Am J Pathol 116:398–406
Ohtsuki I, Watanabe T (1972) Optical diffraction studies on the structure of troponin-tropomyosin-actin paracrystals. J Biochem 72:369–377
Selkoe DJ, Ihara Y, Salazar FJ (1982) Alzheimer's disease: insolubility of partially purified paired helical filaments in sodium dodecyl sulfate and urea. Science 215:1243–1245
Selkoe DJ, Ihara Y, Abraham C, Rasool CG, McCluskey AH (1983) Biochemical and immunocytochemical studies of Alzheimer paired helical filaments. In: Katzman R (ed) Biological aspects of Alzheimer's disease, Banbury report 15. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, pp 125–136
Terry RD, Wisniewski HM (1970) The ultrastructure of the neurofibrillary tangle and the senile plaque. In: Wolstenhome GEW, O'Connor M (eds) Alzheimer disease and related conditions. Churchill, London, pp 145–168
Terry RD, Gonatas NK, Weiss M (1963) The fine structure of neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer's disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 22:629–642
Terry RD, Gonatas NK, Weiss M (1964) Ultrastructural studies in Alzheimer's presenile dementia. Am J Pathol 44:269–297
Tomlinson BE, Blessed G, Roth M (1968) Observations on the brains of non-demented old people. J Neurol Sci 7:331–356
Tomlinson BE, Blessed G, Roth M (1970) Observations on the brains of demented old people. J Neurol Sci 11:205–243
Wisniewski HM, Wen GY (1985) Substructure of paired helical filaments from Alzheimer's disease neurofibrillary tangles. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 66:173–176
Wisniewski HM, Narang HK, Terry RD (1976) Neurofibrillary tanges of paired helical filaments. J Neurol Sci 27:173–181
Wisniewski K, Jervis GA, Moretz RC, Wisniewski HM (1979) Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles in diseases other than senile and presenile dementia. Ann Neurol 5:288–294
Wisniewski HM, Sinatra RS, Iqbal K, Grundke-Iqbal I (1981) Neurofibrillary and synaptic pathology in the aged brain. In: Johnson JE Jr (ed) Aging and cell structure. Plenum, New York, pp 105–141
Wisniewski HM, Merz PA, Iqbal K (1984) Ultrastructure of paired helical filaments of Alzheimer's neurofibrillary tangles. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 43:643–656
Yen SH, Gaskin F, Terry RD (1981) Immunocytochemical studies of neurofibrillary tangles. Am J Pathol 104:77–89
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported in part by the Japanese Ministry of Culture (61570527) and the Research Committee on Senile Dementia of the Ministry of Welfare
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fukatsu, R., Obara, T., Baba, N. et al. Ultrastructural analysis of neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer's disease using computerized digital processing. Acta Neuropathol 75, 519–522 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00687141
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00687141