Abstract
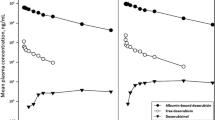
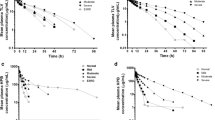
The comparative pharmacokinetics of doxorubicin (DOX) were investigated in five hemodialysis (HD) and eight non-hemodialysis (non-HD) patients who were infused with a 40- to 60-mg dose of DOX at a constant rate over 30 min. A significant difference was observed in the total body clearance (Cl tot) of DOX between HD and non-HD patients. The area under the curve (AUC) for both DOX and doxorubicinol (DOXol), an active metabolite, showed increases of approximately 1.5 and 3 times in HD patients as compared with non-HD patients. Although these differences were not statistically significant (P<0.1), the mean residence time (MRT) of DOX and DOXol in HD patients showed a 2-fold increase in comparison with those in non-HD patients. Compartmental analysis indicated that the greater AUC values and longer MRT of DOX and DOXol in HD patients resulted from the lesser DOXol formation and disappearance of rate constants. As a consequence of the decrease in Cl tot for DOX and the marginal hemodialysis clearance of both DOX and DOXol, the present study suggests that the exposure to DOX and DOXol obtained in HD patients greater that achieved in non-HD patients. Careful attention should therefore be paid to HD patients receiving DOX.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sotherland Ga, Glass J, Gabriel R (1977) Increased incidence of malignancy in chronic renal failure. Nephron 18: 182
Balis FM, Holcenberg JS, Bleyer WA (1983) Clinical pharmaco-kinetics of commonly used anticancer drugs. Clin Pharmacokinet 8: 202
Bachur NR (1979) Anthracycline antibiotic pharmacology and metabolism. Cancer Treat Rep 63: 817
Goto M, Yoshida H, Honda A, Kumazawa T, Ohbayashi T, Inagaki J, Yamanaka N, Ota K (1993) Delayed disposition of Adriamycin and its active metabolite in hemodialysis patients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 44: 301
Ohtsubo K, Aoyama T (1988) High sensitive assay method of DOX in blood by HPLC (abstract, in Japanese). Proc Annu Meet Jpn Pharm Soc 108: 507
Gibaldi M, Perrier D (1982) Application of pharmacokinetic principles and noncompartmental analysis based on statistical moment theory. In: (eds) Pharmacokinetics, 2nd edn. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 385, 409
Loveless H, Arena E, Felsted RL, Bachur NR (1978) Comparative mammalian metabolism of adriamycin and daunorubicin. Cancer Res 38: 593
Yamaoka K, Nakagawa T (1983) A nonlinear least squares program based on differential equations, MULTI [RUNGE], for microcomputers. J Pharmacobiodyn 6: 596
Riggs CE, Benjamin RS, Serpick AA, Bachur NR (1977) Biliary disposition of Adriamycin. Clin Pharmacol Ther 22: 234
Lee HJ, Chiou WL (1989) Erythrocytes as for drug elimination in the isolated rat liver. I. Doxorubicin. Pharm Res 6: 833
Terasaki T, Iga T, Sugiyama Y, Hanano M (1984) Pharmacokinetic study on the mechanism of tissue distribution of doxorubicin: interorgan and interspecies variation of tissue-to-plasma partition coefficients in rats, rabbits, and guinea pigs. J Pharm Sci 73: 1359
Matzke GR, Millikin SP (1992) Influence of renal function and dialysis on drug disposition. In: (eds) Applied pharmacokinetics, 3rd edn. Applied Therapeutics, Inc., Vancouver, Washington, p 8–10
Benjamin RS, Riggs CE, Bachur NR (1977) Plasma pharmacokinetics of Adriamycin and its metabolites in humans with normal and hepatic renal function. Cancer Res 37: 1416
Wilkinson PM (1978) Clinical pharmacology of Adriamycin. In: Pinedo HM (ed) Clinical pharmacology of anti-neoplastic drugs. Elsevier/North-Holland, Amsterdam, p 209
Evans WE, Crom WR, Yee GC, Green AA, Hayes FA, Pratt CB, Avery TL (1980) Adriamycin pharmacokinetics. Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res 21: 176
Koren G, Beaty K, Seto A, Einarson TR, Lishner M (1992) The effects of impaired liver function on the elimination of anti-neoplastic agents. Ann Pharmacother 26: 363
Bachur NR (1975) Adriamycin(NCS-123127) pharmacology. Cancer Treat Rep 6: 153
Bachur NR, Hildebrand RC, Jaenke RS (1974) Adriamycin and daunorubicin disposition in the rabbit. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 191: 331
Chan KK, Cohen JL, Gross JF, Himmelstein KJ, Bateman JR, Tsu-Lee Y, Maris AS (1978) Prediction of Adriamycin disposition in cancer patients using a physiologic, pharmacokinetic model. Cancer Treat Rep 62: 1161
Mross K, Maessen P, Vijgh WJF, Gall H, Boven E, Pinedo HM (1988) Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of epidoxorubicin and doxorubicin in humans. J Clin Oncol 6: 517
Anders MW (1980) Metabolism of drugs by kidney. Kidney Int 18: 636
Touchette MA, Slaughter RL (1991) The effect of renal failure on hepatic drug clearance. Ann Pharmacother 25: 1214
Bianchetti G, Graziani G, Brancaccino D, Morganti A, Leonetti G, Manfrin M, Sega R, Gomeni R, Ponticelli C, Morselli PL (1976) Pharmacokinetics and effects of propranolol in terminal uraemic patients and inpatients undergoing regular dialysis treatment. Clin Pharmacokinet 1: 373
Bateman D, Gokal R, Dodd TRP, Blain PG (1981) The pharmacokinetics of single doses of metoclopramide in renal failure. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 19: 437
Kirch W, Ramsch KD, Duhrsen U, Ohnhaus EE (1984) Clinical pharmacokinetics of nimodipine in normal and impaired renal function. Int J Clin Pharmacol Res 4: 381
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshida, H., Goto, M., Honda, A. et al. Pharmacokinetics of doxorubicin and its active metabolite in patients with normal renal function and in patients on hemodialysis. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 33, 450–454 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00686499
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00686499