Summary
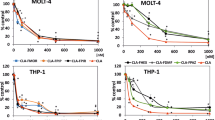
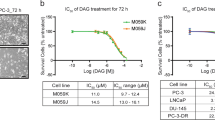
Pretreatment of the human lymphoblastoid cell line CCRF-CEM with 0.02 μm arabinosyl cytosine (ara C) enhances both the cytotoxic and the DNA-damaging effects of etoposide. This concentration of ara C is itself non-cytotoxic and results in no detectable DNA damage as measured by alkaline elution. Ara C pretreatment results in the synchronisation of cells, a 24-h pretreatment resulting in the accumulation of cells in the early S phase. The sensitivity of cells to etoposide-induced cytotoxicity was increased 2.5 times and DNA damage was enhanced 1.66 times by this pretreatment. Maximal potentiation of etoposide-induced DNA damage (2.06-fold increase) was observed after 48 h continuous treatment with ara C, but no further enhancement of cytotoxicity occurred. Cell-cycle analysis demonstrated that 48 h ara C treatment resulted in the accumulation of cells in the late S/G2M phase. Cells returned to a normal cell-cycle distribution within 24 h of the removal of ara C, and the potentiation of etoposide activity was then reduced to a 1.3- to 1.4-fold level. DNA damage induced by etoposide following ara C pretreatment was qualitatively identical to that produced by etoposide alone, suggesting a mechanism involving topoisomerase II. To investigate this possibility, we measured topoisomerase II protein levels by immunoblotting. Measurement of topoisomerase II levels in whole-cell lysates of ara C-pretreated cells showed a 3- to 5-fold increase in topoisomerase levels relative to total protein content. This suggests that elevated enzyme levels may be responsible for the increased sensitivity of ara C-pretreated cells to etoposide.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ara-C:
-
cytosine β-d-arabinofuranoside
- m-AMSA:
-
4′-(9-acridinylamino)-methanesulfon-m-anisidide
- DMSO:
-
dimethylsulphoxide
- MTT:
-
3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide
- SSBs:
-
single-strand breaks
References
Bakic M, Chan D, Andersson BS, Beran M, Silberman L, Estey E, Ricketts L, Zwelling LA (1987) Effect of ara C on nuclear topoisomerase II activity and on the DNA cleavage and cytotoxicity produced bym-AMSA and etoposide inm-AMSA-sensitive and-resistant human leukemia cells. Biochem Pharmacol 36: 4067
Barlogie B, Drewinko B (1978) Cell cycle stage-dependent induction of G2 phase arrest by different antitumour agents. Eur J Cancer 14: 741
Bertrand R, Kerrigan D, Sarang M, Pommier Y (1991) Cell death induced by topoisomerase inhibitors — role of calcium in mammalian cells. Biochem Pharmacol 42: 77
Chen GL, Yang L, Rowe TC, Hallgan BD, Tewey KM, Liu LF (1984) Nonintercalative antitumor drugs interfere with the breakage reunion reaction of mammalian topoisomerase II. J Biol Chem 259: 13560
Chomienne C (1991) Low-dose chemotherapy and differentiating agents. In: Zittun B (ed) Bailliere's clinical haematology. Bailliere Tindall London, p 47
Chow K-C, Ross WE (1987) Topoisomerase-specific drug sensitivity in relation to cell cycle progression. Mol Cell Biol 7: 3119
D'Arpa P, Liu LF (1989) Topoisomerase-targeting antitumor drugs. Biochim Biophys Acta 989: 163
D'Arpa P, Beardmore C, Liu LF (1990) Involvement of nucleic acid synthesis in cell killing mechanisms of topoisomerase poisons. Cancer Res 50: 6919
Dillehay LE, Dentsman SC, Williams JR (1987) Cell cycle dependense of sister chromatid exchange induction by DNA topoisomerase II inhibitors in Chinese hamster V79 cells. Cancer Res 47: 206
Drake FH, Hofmann GA, Bartus HF, Mattern MR, Crooke ST, Mirabelli CK (1989) Biochemical and pharamcological properties of p170 and p180 forms of topoisomerase II. Biochemistry 28: 8154
Edelstein M, Vietti T, Valerote F (1974) Schedule dependent synergism for the combination of 1-β-d-arabinosylcytosine and daunorubicin. Cancer Res 34: 293
Estey E, Adlakna RC, Hittelman WN, Zwelling LA (1987) Cell cycle stage dependent variations in drug-induced topoisomerase II mediated DNA cleavage and cytotoxicity. Biochemistry 26: 4338
Ferguson PJ, Fisher MH, Stephenson J, Li D-L, Zhour B-S, Cheng Y-C (1988) Combined modalities of resistance to etoposide-resistant human KB cell lines. Cancer Res 48: 5956
Fernandes DJ, Smith-Nanni C, Paff MT, Neff T-AM (1988) Effects of antileukemia agents on nuclear matrix-bound DNA replication in CCRF-CEM leukaemia cells. Cancer Res 48: 1850
Fernandes DJ, Danks MK, Beck WT (1990) Decreased nuclear matrix DNA topoisomerase II in human leukemia cells resistant to VM-26 andm-AMSA. Biochemistry 29: 4235
Fram RJ, Kufe DW (1982) DNA strand breaks caused by inhibitors of DNA synthesis: ara C and aphidicolin. Cancer Res 42: 4050
Heck MMS, Hittelman WN, Earnshaw WC (1988) Differential expression of DNA topoisomerase I and II during the eukaryotic cell cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 1086
Horwitz SB, Horwitz MS (1973) Effects of camptothecin on the breakage and repair of DNA during the cell cycle. Cancer Res 33: 2834
Hsiang Y-H, Lihou MG, Liu LF (1989) Arrest of replication forks by drug-stabilised topoisomerase I-DNA cleavable complexes as a mechanism of cell killing by camptothecin. Cancer Res 49: 5077
Jong S de, Zijlstra JG, Vries EG de, Mulder NH (1990) Reduced DNA topoisomerase II activity and drug-induced DNA cleavage activity in an Adriamycin-resistant human small cell lung carcinoma cell line. Cancer Res 50: 304
Kaufmann SH (1989) Induction of endonucleolytic DNA cleavage in human acute myelogenous leukemia cells by etoposide, camptothecin, and other cytotoxic anticancer drugs: a cautionary note. Cancer Res 49: 5870
Kohn KW, Erickson LC, Ewig RAG, Friedman CA (1976) Fractionation of DNA from mammalian cells by alkaline elution. Biochemistry 15: 4629
Kufe DW, Munroe D, Herrick DJ, Egan M, Spriggs D (1984) Effects of 1-β-d-arabinosylcytosine incorporation on eukaryotic DNA template function. Mol Pharmacol 26: 128
Lazzarino M, Morra E, Inverardi D, Alessandrino EP, Castelli G, Bernasconi P, Castagnoia C, Bernasconi C (1986) Combined etoposide and cytarabine for acute myelogenous leukaemia's evolving from myelodysplastic syndrome secondary to treatment for malignant diseases (abstract). Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 5: 161
Liu LF (1989) DNA topoisomerase poisons as antitumor drugs. Annu Rev Biochem 58: 351
Liu LF, Rowe TC, Yang L, Tewey KM, Chen GL (1983) Cleavage of DNA by mammalian DNA topoisomerase II. J Biol Chem 258: 15365
Lorico A, Boiocchi M, Rappa G, Sen S, Erba E, D'Incalci M (1990) Increase in topoisomerse-II-mediated DNA breaks and cytotoxicity of VP16 in human U937 lymphoma cells pretreated with low doses of methotrexate. Int J Cancer 45: 156
Major PP, Egan M, Herrick DJ, Kufe DW (1982) Effects of ara C incorporation on DNA synthesis in L1210 cells. Biochem Pharmacol 31: 2937
Markovits J, Pommier Y, Kerrigan D, Covey JM, Tilchen EJ, Kohn KW (1987) Topoisomerase II-mediated DNA breaks and cytotoxicity in relation to cell proliferation and the cell cycle in NIH 3T3 fibroblasts and L1210 leukemia cells. Cancer Res 47: 2050
Meyn RE, Meistrich ML, White RA (1980) Cycle-dependent anticancer drug cytotoxicity in mammalian cells synchronised by centrifugal elutriation. J Natl Cancer Inst 64: 1215
Minford J, Kerrigan D, Nichols M, Shackney S, Zwelling LA (1984) Enhancement of the DNA breakage and cytotoxic effects of intercalating agents by treatment with sublethal doses of 1-β-d-arabinofuranosyl cytosine or hydroxyurea in L1210 cells. Cancer Res 44: 5583
Mossman T (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65: 55
Nelson EM, Tewey KM, Liu LF (1984) Mechanism of antitumour drug action: poisoning of mammalian DNA topoisomerase II on DNA by 4′-(9-acridinylamino)-methansulfon-m-anisidide. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81: 1361
Pommier Y, Schwartz RE, Zwelling LA, Kerrigan D, Mattern MR, Charcosset JY, Jacquemin-Sablon A, Kohn KW (1986) Reduced formation of protein-associated DNA strand breaks in Chinese hamster cells resistant to topoisomerase inhibitors. Cancer Res 46: 611
Pommier Y, Kerrigan D, Schwartz RE, Swack JA, McCurdy A (1986) Altered DNA topoisomerase II activity in Chinese hamster cells resistant to topoisomerase inhibitors. Cancer Res 46: 3075
Rivera G, Avery T, Roberts deW (1975) Response of L1210 to combinations of cytosine arabinoside and VM26 or etoposide. Eur J Cancer 11: 639
Ross WE, Rowe TC, Glisson BS, Yalowich JC, Liu LF (1984) Role of topoisomerase II in mediating epipodophyllotoxin-induced DNA cleavage. Cancer Res 44: 5857
Schneider E, Lawson PA, Ralph RK (1989) Inhibition of protein synthesis reduces the cytotoxicity ofm-AMSA without affecting DNA breakage and DNA topoisomerase II in a murine mastocytoma cell line. Biochem Pharmacol 38: 263
Sullivan DM, Glisson BS, Hodges PK, Smallwood-Kentro S, Ross WE (1986) Proliferation dependence of topoisomerase II mediated drug action. Biochemistry 25: 2248
Sullivan DM, Latham MD, Ross WE (1987) Proliferation dependent topoisomerase II content as a determinant of antineoplastic drug action in human, mouse and Chinese hamster ovary cells. Cancer Res 47: 3973
Taudou G, Mirambeau G, Lavenor C, Garabedian A, Vemeersch J, Duguet M (1984) DNA topoisomerase activities in concanavalin A-stimulated lymphocytes. FEBS Lett 176: 431
Tewey KM, Chen GL, Nelson EM, Liu LF (1984) Intercalative antitumor drugs interfere with the breakage-reunion reaction of mammalian topoisomerase II. J Biol Chem 259: 9182
Utsumi H, Shibuya ML, Kosaka T, Buddenbaum WE, Elkind MM (1990) Abrogation by novobiocin of cytotoxicity due to the topoisomerase II inhibitor amsacrine in Chinese hamster cells. Cancer Res 50: 2577
Woessner RD, Mattern MR, Mirabelli CK, Johnson RK, Drake FH (1991) Proliferation- and cell cycle-dependent differences in expression of the 170 kilodalton and 180 kilodalton forms of topoisomerase II in NIH-3T3 cells. Cell Growth Differ 2: 209
Zhang H, D'Arpa P, Liu LF (1990) A model for tumor cell killing by topoisomerase poisons. Cancer Cells 2: 23
Zwelling LA, Hinds M, Chan D, Altschuler E, Mayes J, Zipf TF (1990) Phorbol ester effects on topoisomerase activity and gene expression in HL-60 human leukemia cells with different proclivities toward monocytoid differentiation. Cancer Res 50: 7116
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by a grant from the North East Thames Regional Health Authority
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chresta, C.M., Hicks, R., Hartley, J.A. et al. Potentiation of etoposide-induced cytotoxicity and DNA damage in CCRF-CEM cells by pretreatment with non-cytotoxic concentrations of arabinosyl cytosine. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 31, 139–145 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00685101
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00685101