Abstract
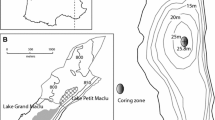
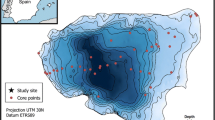
In paleolimnology, subfossil head capsules of chironomids play an important role as ecological indicators of lake history. It is important to determine, therefore, whether fossil assemblages are representative of former biocoenoses. There is evidence that headcapsules washed in from other places can make up a significant percentage of the total. As interpretations are usually drawn from the examination of a single core, it is of special interest to know whether a fossil assemblage of a single site properly reflects limnological conditions of the whole lake. This study examined the taxonomic distribution of subfossil chironomids in the surficial sediments of the Bodensee-Untersee, with the aim of assessing the variability in chironomid assemblages. Apparently, most of the head capsules of the profundal fossil assemblages in the Untersee had been washed in from the littoral zone or from the slope. Although the Bodensee-Untersee is a rather large lake, variability is surprisingly low among all samples. Therefore a correct interpretation from a single core may be possible.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brundin, L., 1949. Chironomiden und andere Bodentiere der südschwedischen Urgebirgsseen. Ein Beitrag zur Kenntnis der bodenfaunistischen Charakterzüge schwedischer oligotropher Seen. Rep. Inst. Freshw. Res. Drottningholm 30: 1–914.
Brundin, L., 1956. Die bodenfaunistischen Seentypen und ihre Anwendbarkeit auf die Südhalbkugel. Zugleich eine Theorie der produktionsbiologischen Bedeutung der glazialen Erosion. Rep. Inst. Freshw. Res. Drottningholm 37: 186–235.
Davis, M. B., R. E. Moeller & J. Ford, 1984. Sediment focusing and pollen influx. In E. Y. Harworth & J. W. G. Lund (eds), Lake sediments and environmental History. Leicester Univ. Press: 261–293.
Hofmann, W., 1971a. Die postglaziale Entwicklung der Chironomiden- undChaoborus-Fauna (Dipt.) des Schöhsees. Arch. Hydrobiol. Suppl. 40: 1–74.
Hofmann, W., 1971b. Zur Taxonomie und Palökologie subfossiler Chironomiden (Dipt.) in Seesedimenten. Arch. Hydrobiol. Beih. Ergebn. Limnol. 6: 1–50.
Hofmann, W., 1979. Chironomid analysis. In B. E. Berglund (ed.), Palaeohydrological changes in the temperate zone in the last 15000 years. Subproject B. Lake and mire environments. 2. Lund: International Geological Correlation Programme 1979. (Project 158.): 259–270.
Huhta, V., 1979. Evaluation of different similarity indices as measures of succession in arthropod communities of the forest floor after clear-cutting. Oecologia 41: 11–23.
Int. Gewässerschutzkomm. Bodensee, 1967. Die Temperaturund Sauerstoffverhältnisse des Bodensees in den Jahren 1961–1963. Internationale Gewässerschutzkommission für den Bodensee, Bericht Nr. 5, Germany, 128 pp.
Int. Gewässerschutzkomm. Bodensee, 1975. Zustand und neuere Entwicklung des Bodensees. Internationale Gewässerschutzkommission für den Bodensee, Bericht Nr. 16, Germany, 33 pp.
Int. Gewässerschutzkomm. Bodensee, 1989. Die langjährige Entwicklung des Phytoplanktons im Bodensee (1961–1986). Internationale Gewässerschutzkommission für den Bodensee, Bericht Nr. 39, Germany, 175 pp.
Likens, G. E. & M. B. Davis, 1975. Post-glacial history of Mirror Lake and its watershed in New Hampshire USA: an initial report Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 19: 982–993.
Müller, G., 1966. Die Sedimentbildung im Bodensee. Die Naturwissenschaften 53: 237–247.
Pinder, L. C. V. & F. Reiss, 1983. The larvae of Chironominae (Diptera: Chironomidae) of the Holarctic region — keys and diagnoses. In T. Wiederholm (ed.), Chironomidae of the Holarctic region. Keys and diagnoses. Part I. Larvae. Ent. scand. Suppl. 19: 293–435.
Reiss, F., 1968. Ökologische und systematische Untersuchungen an Chironomiden (Diptera) des Bodensees. Ein Beitrag zur lakustrischen Chironomidenfauna des nördlichen Alpenvorlandes. Arch. Hydrobiol. 64: 176–323.
Renkonen, O., 1938. Statistisch-ökologische Untersuchungen über die terrestrische Käferwelt der finnischen Bruchmoore. Ann. Zool. Soc. Zool.-Bot. Fenn. Vanamo 6: 1–231.
Sæther, O.A., 1975. Nearctic chironomids as indicators of lake typology. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 19: 3127–3133.
Sæther, O. A., 1979. Chironomid communities as water quality indicators. Holarct. Ecol. 2: 65–74.
Schröder, R., 1974. Strömungsverhältnisse im Bodensee-Untersee und der Wasseraustausch zwischen den einzelnen Seebecken. Internationale Gewässerschutzkommission für den Bodensee, Bericht Nr. 15, Germany, 24 pp.
Sneath, P. H. A. & R. R. Sokal, 1973. Numerical taxonomy. Freeman & Co., San Francisco, 573 pp.
Southwood, T. R. E., 1966. Ecological methods. Butler & Tanner, London, 391 pp.
Stahl, J. B., 1969. The uses of chironomids and other midges in interpreting lake histories. Mitt. int. Ver. Limnol. 17: 111–125.
Thienemann, A., 1920. Untersuchungen über die Beziehungen zwischen dem Sauerstoffgehalt des Wassers und der Zusammensetzung der Fauna in norddeutschen Seen. Arch. Hydrobiol. 12: 1–65.
Thienemann, A., 1954.Chironomus. Leben, Verbreitung und wirtschaftliche Bedeutung der Chironomiden. Binnengewässer 20: 1–834.
Walker, I. R. & C. G. Paterson, 1985. Efficient separation of subfossil Chironomidae from lake sediments. Hydrobiologia 122: 189–192.
Wiederholm, T. (ed.), 1983. Chironomidae of the Holarctic region. Keys and Diagnoses. Part 1. Larvae. Ent. scand. Suppl. 19: 1–457.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmäh, A. Variation among fossil chironomid assemblages in surficial sediments of Bodensee-Untersee (SW-Germany): implications for paleolimnological interpretation. J Paleolimnol 9, 99–108 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00677512
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00677512