Summary
Alterations in the morphology of the endometrial layers and in the pattern of their DNA-synthesis were studied in 28 human females (25–48 years) who had received the sequential oral contraceptive Ovanon®, (7 days mestranol, followed by 15 days mestranol in combination with lynestrenol) 15 months each totalizing 305 cycles.
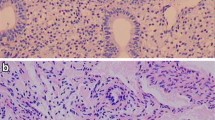
Morphological investigations of 97 biopsies of the endometrium yielded more appropriate changes of glands and stroma with the normophasic sequential treatment, compared with monophasic contraceptives. Tissue proliferated in the presence of estrogene component (0.08 mg mestranol). The subsequently applied combination of estrogenes and gestagenes (0.07 mg mestranol +2.5 mg lynestrenol) effected pseudo-secretory changes. After prolonged use (from 7th cycle) serpentines of the tubular glands during the first half of the cycle gradually decreased.
During secretion phase the changes indicated abortive secretion with involution of tubular glands. The appearance was dominated from 8th to 18th day of cycle by a spotted stromal edema. At the end of the cycle venous ectasias appeared together with spiral arteries, displaying endothelial hyperplasia and proliferation. Moreover glandular and stromal atrophy could be observed, but did not increase with prolongation of treatment. It is suggested that such an endometrium is not apt for nidation of a fertilized ovulum. Proliferative activity of the Ovanon-treated endometrial tissue was studied by radioautography using3H-thymidin. Based on silver grain counts in different layers of the endometrium, DNA-synthesis pattern was similar in the gland epithelium and in the superficial epithelium in the proliferative phase. No DNA-synthesis was found during the secretion phase.
Thymidin incorporation was observed during all cyclic phases in the stroma. It is concluded that permanent application of the hormone for 15 months does not result in significant changes of the endometrial DNA-synthesis pattern.
Zusammenfassung
Bei 28 Patientinnen zwischen 25 und 48 Jahren wurde der normophasische Ovulationshemmer Ovanon® (Mestranol und Mestranol in Kombination mit Lynestrenol), Sequenzfolge 7+15, hinsichtlich seiner morphologischen Veränderungen am Endometrium und seiner Beeinflussung der DNS-Synthese in den Einzelabschnitten des Endometriums untersucht. Die Patientinnen wurden während 305 Cyclen über 15 Monate beobachtet.
Die morphologischen Untersuchungen des Endometriums anhand von 97 Endometriumbiopsien ergaben unter der normophasischen Sequenzbehandlung cyolusgerechtere Veränderungen von Stroma und Drüsen als bei der Kombinationstherapie. Unter dem 7tägigen Einfluß der Oestrogenkomponente (0,08 mg Mestranol) proliferierte das Gewebe. Die anschließend mit Oestrogenen verabreichten Gestagene (0,075 mg Mestranol und 2,5 mg Lynestrenol) bewirkten pseudosekretorische Veränderungen. Bei längerer Einnahmedauer (ab 7. Cyclus) sah man in der ersten Cyclushälfte trotz vorhandener epithelialer Proliferation zunehmend geringere Schlängelung der Drüsenschläuche. In der Sekretionsphase entsprechen die Veränderungen einer abortiven Sekretion mit involutierten Drüsenschläuchen. Zwischen dem 8. und 18. Cyclustag herrschte das Bild des fleckigen Stromaödems vor. Am Ende des Cyclus traten Venektasien und Spiralarterien mit Endothelhyperplasie und -proliferation auf. Außerdem wurde häufig eine Drüsen- und Stromaatrophie festgestellt, die jedoch bei zunehmender Behandlungsdauer keine Verstärkung aufwies. Für die Nidation eines befruchteten Eies scheint ein solches Endometrium nicht geeignet zu sein. Die Proliferationsaktivität des mit Ovanon behandelten Endometriums wurde durch die autoradiographische Methode mit3H-Thymidin untersucht. Aufgrund der Bestimmungen der3H-Indices der Einzelabschnitte des Endometriums fand sich ein ähnliches Verhalten der DNS-Synthese im Drüsenepithel und im Oberflächenepithel in der Proliferationsphase. In der Sekretionsphase war keine DNS-Synthese nachweisbar. Im Stroma dagegen ließ sich während aller Cyclusphasen Proliferationstätigkeit finden.
Trotz der andauernden Hormonzufuhr im Laufe von 15 Behandlungsmonaten wurde keine statistisch signifikante Änderung der DNS-Synthese im Endometrium festgestellt.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Adinolfi, G., Ferrari, V.: Zit. nach Schmidt-Matthiesen. Das normale menschliche Endometrium, S. 170. Stuttgart: Thieme 1963.
Ahrnes, C. A., Prinz, G.: Mitosen im Endometrium. Geburtsh. u. Frauenheilk.17, 475–483 (1957).
Ancla, M., Simon, P., Brux, J. de., Robey, M.: Endometriumveränderungen nach Langzeitbehandlung mit Lynestrenol. Gynéc. et Obstet.64, 231–250 (1965).
Bélanger, L. F., Leblond, C. P.: A method for location radioactive elements in tissues by covering histological sections with a photographic emulsion. Endocrinology39, 8–13 (1946).
Blaustein, A., Shenker, L., Post, R. C.: The effects of oral contraceptives on the endometrium. Int. J. Teril.13, 466–475 (1968).
Boquoi, E., Beato, M., Ebner, H., Sandritter, W.: DNS-Gehalt und3H-Thymidineinbau des Endometriums der weißen Maus während des normalen Cyclus nach Kastration und unter Östrogen-Gestagen-Behandlung. Arch. Gynäk.206, 181–194 (1968).
Boquoi, E., Müller, J. E.: Ein Beitrag zur Frage der Wirkung von sog. Ovulationshemmern auf das Epithel von Cervix uteri und Vagina. Zbl. Gynäk.89, 1318–1323 (1967).
Bremer, E., Ober, K. G., Zander, J.: Histochem. Untersuchungen über das Verhalten der Nucleinsäuren im Endometrium. Arch. Gynäk.181, 96–108 (1951).
Brody, S., Westman, A.: Effects of oestradiol and progesterone on the acids and protein content of the rabbit uterus. Acta Endocr.27, 493 (1958).
Dallenbach-Hellwig, G.: Endometrium. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1969.
Fettig, O.: Autoradiograph. Untersuchungen zur DNS-, RNS- und Proteinsynthese am Portioepithel und Endometrium der Frau. Habilitationsarbeit 1964.
Fettig, O.: Autoradiograph. Untersuchungen der DNS-, RNS- und Proteinsynthese im menschl. Endometrium in Abhängigkeit von der Ovulation. Arch. Gynäk.202, 246–248 (1965).
Fettig, O.:3H-Index-Bestimmungen und Berechnungen der mittleren Generationszeit (Lebensdauer) der Einzelabschnitte nach autoradiograph. Untersuchungen mit3H-Thymidin des gesunden und krankhaften Endometriums. Arch. Gynäk.200, 659–677 (1965).
Fettig, O., Hillemanns, H. G., Kopecky, P.: Erfahrungen mit der Sequenztherapie. Geburtsh. u. Frauenheilk.28, 975–976 (1968).
Fettig, O., Kopecky, P.: Klinische und morphologische Untersuchungen zur hormonellen Antikonzeption mit der Sequentialmethode. Geburtsh. u. Frauenheilk.28, 540–553 (1968).
Fettig, O., Oehlert, W.: Autoradiograph. Untersuchungen der DNS- und Eiweißneubildung im gynäkolog. Untersuchungsmaterial. Arch. Gynäk.199, 649–662 (1964).
Friedrich, E. R.: Effects of contraceptive hormone preparations on the fine structure of the endometrium. Obstet. and Gynec.30, 201 (1967).
Goldzieher, J. W., Becerra, C., Gual, C., Livingstone, N. B., Maqueo, M., Moses, L. L. E., Tietze, Ch.: New oral contraceptive sequential estrogen and progestin. Amer. J. Obstet. Gynec.90, 404–441 (1964).
Hahn, W. E., Church, R. B., Gorbman, A., Wilmot, L.: Estrone- and progesteroneinduced synthesis of new RNA species in the chick oviduct. Gen. comp. Endocr.10, 438–442 (1968).
Hamilton, R. H.: Control by estrogen of genetic transcription. Science161, 649–661 (1968).
Maqueo, M., Becerra, C., Mungia, H., Goldzieher, J. W.: Endometrial histology and vaginal cytology during oral contraception with sequential estrogen and progestin. Amer. J. Obstet. Gynec.98, 395–400 (1964).
Maqueo, M., Perez-Vega, E., Goldzieher, J. W., Martinez-Manautou, J., Rudel, H.: Comparison of the endometrial activity of 3-synthetic progestins used in fertility control. Amer. J. Obstet. Gynec.85, 427–432 (1963).
McKern, K. W.: Genetic, biochemical and hormonal mechanism in the regulation of uterine metabolism. In: Cellular biology of the uterus, p. 71–113, ed. R. Wynn. Amsterdam: North Holland 1967.
Norquist, S.: The synthesis of DNA and RNA in normal human endometrium in short-term incubation in vitro and its response to oestradiol and progesterone. J. Endocr.48, 17–28 (1970).
Noyes, R. W., Hertig, A. T., Rock, J.: Dating the endometrial biopsy. Fertil. and Steril.1, 3 (1950).
Ober, W. B.: Synthetic progestagen-oestrogen preparations and endometrial morphology. J. clin. Path.19, 138–147 (1966).
Ober, W. B., Decker, A., Clyman, M. J., Roland, M.: Endometrial morphology after sequential medication with mestranol and chlormadinone. Obstet. and Gynec.28, 247–253 (1966).
Oehlert, W., Lesch, R., Dormer, P.: Autoradiograph. Untersuchungen des DNS-, RNS-Stoffwechsels am menschlichen Excisionsmaterial. Naturwissenschaften23, 713–714 (1963).
O'Malley, B. W., McGuire, W. L.: Studies on the mechanism of action of progesterone in regulation of the synthesis of specific protein. J. clin. Invest.47, 654–664 (1968).
Pinero, O., Foraker, A. G.: DNA and RNA in normal human endometrium. Amer. J. Obstet. Gynec.89, 657–660 (1964).
Schmidt-Matthiesen, H.: Das normale menschliche Endometrium. Stuttgart: Thieme 1963.
Segal, S. J., Scher, W.: Estrogens, nucleic acids and protein synthesis in uterine metabolism. In: Cellular biology of the uterus, p. 114–150, ed. R. M. Wynn. Amsterdam: North Holland 1967.
Song, J., Mark, M., Lawler, M. P.: Endometrial changes in women receiving oral contraceptives. Amer. J. Obstet. Gynec.107, 717–728 (1970).
Sturgis, S. H., Meigs, J. V.: Endometrial cycle and mechanism of normal menstruation. Amer. J. Surg.33, 369 (1936).
Tata, J. R.: Hormonal regulation of growth and protein synthesis. Nature (Lond.)219, 331–337 (1968).
Vokaer, R., Gompel, C., Ghilain, A.: Variations in the content of DNA in the humane uterine and in vaginal receptors during the menstrual cycle. Nature (Lond.)172, 31–32 (1953).
Wagner, D., Richart, R., Terner, J. Y.: DNA-content of human endometrial gland cells during the menstrual cycle. Amer. J. Obstet. Gynec.100, 90–97 (1968).
Waidl, E., Fikentscher, H., Bruckner, W.: Die intercellulären Strukturen des Endometriums bei der oralen Kontrazeption. Geburtsh. u. Frauenheilk.28, 159 (1968).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaltenbach, F.J., Fettig, O. & Welter, J. Histologische und autoradiographische Untersuchungen am menschlichen Endometrium unter der 2-Phasen-Therapie mit Mestranol-Lynestrenol. Arch. Gynak. 215, 325–342 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00672816
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00672816