Summary
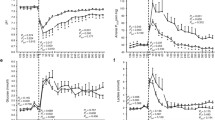
The influence of pathological situations to fetal lung maturation during the last 9 weeks of pregnancy was studied. Lung maturity was determined by four different methods, analyzing the concentration of surfactant in amniotic fluid. L/S ratio was measured planimetrically and densitometrically, foam test and surface tension of the liquor amnii were used on this purpose. 89 normal pregnancies for obtaining normal values served as a basis for comparison with pathological events. A general retardation of fetal lung maturity showed 26 patients with rhesus isoimmunization so as 26 patients with diabetes classes A, B and C (White). In three pregnancies complicated by diabetes class D a remarkable acceleration of fetal lung maturity was obvious. 30 patients with placental insufficiency sui generis presented a very inhomogenous development of the fetal lung, whereas in 35 patients with EPH-gestosis a minute acceleration between 33th and 37th week of gestation was found. A good correlation between all of the used methods for measuring the concentration of surfactant was noted. Best reliability in correct prediction of lung maturity showed the method of measuring the surface-tension of the amniotic fluid.
Zusammenfassung
Der Einfluß pathologischer Situationen in den letzten 9 Wochen der Schwangerschaft auf die Reifung der fetalen Lunge wurde geprüft. Dabei kamen zur Bestimmung der fetalen Lungenreife folgende Methoden zum Einsatz: Dünnschichtchromatographischer Nachweis von Lecithin und Sphingomyelin mit anschließender planimetrischer oder densitometrischer Auswertung zur Bildung einer L/S-Ratio. Weiters wurden die gesättigten Phosphatidylcholine im Fruchtwasser mittels des Clements-Foam-Tests bestimmt. Als vierte Bestimmungsmethode war die Messung der Oberflächenspannung des Fruchtwassers mittels Wilhelmy-Waage im Einsatz. Aus 89 normal verlaufenden Schwangerschaften wurden Normverlaufskurven für die einzelnen Bestimmungsverfahren erstellt und diese dienten als Vergleichsbasis zu den bei pathologischen Schwangerschaften erhaltenen Werten. 26 Fälle von Rhesusinkompatibilität wiesen eine allgemeine Retardierung der Lungenreife ebenso wie 26 Fälle diabeteserkrankter Mütter der Klassen A, B und C nach White auf. Drei Fälle von Diabetes der Klasse D nach White zeigten Werte erhöhter Surfactantkonzentration. 30 Fälle von Plazentainsuffizienz sui generis boten ein Bild inhomogener Entwicklung der fetalen Lungenreife, während 35 Fälle mit EPH-Gestose bis auf eine leichte Akzeleration zwischen der 33. und 37. Schwangerschaftswoche eine unauffällige Lungenreifung des Feten boten. Anschließend wurden sämtliche Meßwerte miteinander statistisch korreliert.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Bayer, H., Bonnar, J., Phizackerley, P. J. R., Moore, R. A., Wylie, F.: Amniotic fluid phospholipids in normal and abnormal pregnancy. J. Obstet. Gynec. Brit. Cwlth80, 333 (1973)
Caspi, E., Schreyer, P., Weinraub, Z., Bukovksy, I., Tamir, I.: Changes in amniotic lecithin-sphingomyelin ratio following maternal Dexamethasone administration. Amer. J. Obstet. Gynec.122, 327 (1975)
Cleary, R. E., Young, C. M.: Serum unconjugated estriol in normal and abnormal pregnancy. Amer. J. Obstet. Gynec.118, 18 (1974)
Clements, J. A., Platzker, A. C. G., Tierney, D. F., Hobel, C. J., Creasy, R. K., Margolis, A. J., Thibeault, D. W., Tooley, W. H., Oh, W.: Assessment of the risk of the respiratory distress syndrome by a rapid test for surfactant in amniotic fluid. New Engl. J. Med.286, 1077 (1972)
Duhring, J. L., Thompson, S. A.: Amniotic fluid phospholipid analysis in normal and complicated pregnancies. Amer. J. Obstet. Gynec.121, 218 (1975)
Dunn, L. J., Bhatnagar, A. S.: Use of lecithin/sphingomyelin ratio in the management of the problem obstetric patient. Amer. J. Obstet. Gynec.115, 687 (1973)
Dyson, D., Blake, M., Cassady, G.: Amniotic fluid lecithin-sphingomyelin ratio in complicated pregnancies. Amer. J. Obstet. Gynec.122, 772 (1975)
Falconer, G. F., Hodge, J. S., Gadd, R. L.: Influence of amniotic fluid volume on lecithin estimation in prediction of respiratory distress. Brit. med. J.2, 689 (1973)
Gerner, R., Halberstadt, E.: Die Wirkung von Bromhexine Metabolit VIII auf die Lecithinsynthese in der fetalen Lunge. Z. Geburtsh. Perinat.181, 80 (1977)
Gluck, L., Kulovich, M. V.: Lecithin/sphingomyelin ratio in amniotic fluid in normal and abnormal pregnancy. Amer. J. Obstet. Gynec.115 (4), 539 (1973)
Gluck, L., Kulovich, M. V., Borer, R. C., Keidel, W. N.: The interpretation and significance of the lecithin-sphingomyelin ratio in amniotic fluid. Amer. J. Obstet. Gynec.120, 142 (1974)
Goecke, C., Schwabe, G.: Vorschlag einer Stadieneinteilung der Gestose. Zbl. Gynäk. 1439 (1965)
Goldenberg, R. L., Nelson, K.: Iatrogenic respiratory distress syndrome. Amer. J. Obstet. Gynec.123, 617 (1975)
Gould, J. B., Gluck, L., Kulovich, M. V.: The acceleration of neurological maturation in high stress pregnancy and its relation to fetal lung maturity. Pediat. Res.6, 276 (1972)
Graven, S. N., Misenheimer, H. R.: Respiratory distress syndrome and the high risk mother. Amer. J. Dis. Child.109, 489 (1965)
Gruenwald, P.: Chronic fetal distress and placental insufficiency. Biol. Neonat. (Basel)5, 215 (1963)
Hobel, C. J., Oh, W., Hyvarinen, M. A., Emmanoulides, G. C., Ehrenberg, A.: Early versus late treatment of neonatal acidosis in low birth weight infants: Relation to respiratory distress syndrome. J. Pediat.81, 1178 (1972)
Jackson, R. W., Anderson, G. D., Held, B.: Amniotic fluid phospholipids and fetal lung maturity. 1. Assessment of various methods of determining lecithin and sphingomyelin. Amer. J. Obstet. Gynec.121, 1089 (1975)
Janisch, H., Leodolter, S.: Estimation of placental function by measuring the HPL serum level and recording the placental flow. J. Perinat. Med.1, 283 (1973)
Kalbac, R. W., Newman, R. L.: Amniotic fluid analysis in complicated pregnancies. Obstet. and Gynec.44, 814 (1974)
Kubli, F.: Die chronische Plazentarinsuffizienz. Gynäkologe1, 53 (1968)
Leodolter, S.: Neue Gesichtspunkte zur Erfassung und Behandlung der Plazentainsuffizienz. Wien. klin. Wschr.89 (Suppl. 70), 9 (1977)
Liley, A. W.: Liquor amnii analysis in the management of the pregnancy complicated by rhesus sensitization. Amer. J. Obstet. Gynec.82, 1359 (1961)
Lindback, T., Frantz, T., Skjaeraasen, J., Graven, S.: Phospholipids in amniotic fluid. Acta obstet. gynec. scand.53, 219 (1974)
Lorenz, U., Rüttgers, H., Fux, G., Kubli, F.: Fetal pulmonary surfactant induction by bromhexine metabolite VIII. Amer. J. Obstet. Gynec.119, 1126 (1974)
Masson, D., Diedrich, K., Rehm, G., Stefan, M., Schultze-Mosgau, H.: Die Messung der Oberflächenspannung im Fruchtwasser als einfache Methode zur Bestimmung der fetalen Lungenreife. Geburtsh. u. Frauenheilk.37, 57 (1977)
Müller-Tyl, E., Lempert, J.: The prediction of fetal lung maturity from the surface tension characteristics of amniotic fluid. J. Perinat. Med.3, 47 (1975)
Müller-Tyl, E., Lempert, J., Janisch, H., Leodolter, S.: Placentafunktion und fetale Lungenreife. Wien. klin. Wschr.87, 277 (1975)
Müller-Tyl, E., Lempert, J., Salzer, H., Altmann, P.: Oberflächeneigenschaften des Fruchtwassers im Verlauf einzelner Schwangerschaften anhand von Serienpunktionen. Geburtsh. u. Frauenheilk.37, 718 (1977)
Müller-Tyl, E., Lempert, J., Steinbereithner, K., Benzer, H.: Surface properties of the amniotic fluid in normal pregnancy. Amer. J. Obstet. Gynec.122, 295 (1975)
Müller-Tyl, E., Salzer, H., Altmann, P., Müller, M. M.: Verschiedene Bestimmungsmethoden des Surfactantgehaltes des Fruchtwassers im Einsatz bei Serien-Untersuchungen an Schwangeren. Z. Geburtsh. Perinat.181, 251 (1977)
Nelson, G. H.: Amniotic fluid phospholipid patterns in normal and abnormal pregnancies. Amer. J. Obstet. Gynec.105, 1072 (1969)
Nelson, G. H.: Risk of respiratory distress syndrome as determined by amniotic fluid lecithin concentration. Amer. J. Obstet. Gynec.121, 753 (1975)
Nelson, G. H., Lawson, S. W.: Determination of amniotic fluid total phospholipid phosphorus as a test for fetal lung maturity. Amer. J. Obstet. Gynec.115, 933 (1973)
Phelps, D. L.: Intrauterine stress and pulmonary maturation. J. Pediat.85, 879 (1974)
Polishuk, W. Z., Anteby, S., Bar-On, H., Stein, Y.: Lecithin/sphingomyelin ratio in amniotic fluid of diabetic mothers: A warning of respiratory distress in newborn? Lancet1973 I, 36
Rüttgers, H., Lorenz, U., Schütz, W., Winkler, J., Kubli, F.: Vergleich von physikalischen und biochemischen Methoden zur antepartalen Reife-Diagnostik der fetalen Lunge aus dem Fruchtwasser. In: Perinatale Medizin V, S. 117. Stuttgart: Thieme 1974
Schwenzel, W., Jung, H.: Pränatale Behandlungsmethoden zur Vermeidung eines Atemnotsyndroms bei frühgeborenen Kindern. Gynäkologe8, 198 (1975)
Shephard, B., Buhi, W. C., Spellacy, W.: Critical analysis of the amniotic fluid shake-test. Obstet. and Gynec.43, 558 (1974)
Siebert, W., Meitinger, C.: Prophylaxe des Atemnotsyndroms mit Betamethason. Geburtsh. u. Frauenheilk.35, 130 (1975)
Silvermann, W. A.: Dunham's premature infants. New York: Hoeber 1971
Spellacy, W. N., Buhi, W. C.: Amniotic fluid lecithin/sphingomyelin ratio as an index of fetal maturity. Obstet. and Gynec.39, 852 (1972)
Thibeault, D. W., Hobel, C. J.: The interrelationship of the foam stability test, immaturiry, and intrapartum complications in the respiratory distress syndrome. Amer. J. Obstet. Gynec.118, 56 (1973)
White, P.: Pregnancy and diabetes, medical aspects. Med. Clin. N. Amer.49, 1015 (1963)
White, P.: Pregnancy complicating diabetes. In: The treatment of Diabetes mellitus (Joslin, E. P., ed.). Philadelphia 1959
Whitfield, C. R., Sproule, W. B., Brudenell, M.: The amniotic fluid lecithin: sphingomyelin area ratio (LSAR) in pregnancies complicated by diabetes. J. Obstet. Gynec. Brit. Cwlth80, 918 (1973)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Müller-Tyl, E., Salzer, H. Fetale Lungenreife bei pathologischen Schwangerschaften. Arch. Gynak. 225, 109–122 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00670847
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00670847