Conclusions
-
1.
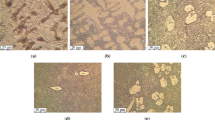
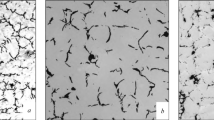
Alloying of cast iron with chromium and nickel is inadvisable for parts needing high resistance to creep and relaxation at 400–500°.
-
2.
For cast iron working at temperatures up to 330° the addition of chromium is desirable, since it stabilizes pearlite and hardens the cast iron.
-
3.
At a concentration of ∼0.2%, titanium substantially increases the resistance of cast iron to creep and relaxation at all temperatures investigated (330, 400, 520°).
Similar content being viewed by others
Additional information
Gor'kii Polytechnical Institute. Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 6, pp. 67–69, June, 1970.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kozhinskii, L.I. Effect of chromium and titanium on creep and relaxation of cast iron. Met Sci Heat Treat 12, 527–529 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00668871
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00668871