Abstract
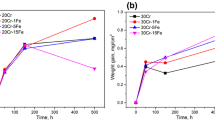
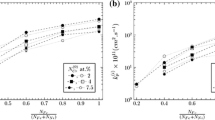
The effects of aluminum and titanium additions on the oxidation and carburization behavior of Fe-21%Cr-32%Ni in an HTGR-simulated impure helium environment at high temperatures were studied. Intragranular and intergranular oxidation were the principal forms of degradation, with the effect of aluminum being major and that of titanium relatively minor. As the aluminum content in the alloy increased, the mode of degradation changed from both uniform intragranular and intergranular oxidation, to one involving only uniform intragranular oxidation. This transition in the degradation mode was explained by the volume changes in the alloy resulting from a combination of both a volume increase due to internal-oxide precipitation and shrinkage due to the condensation of vacancies formed as a result of selective removal of alloying elements to the external scale. Intergranular oxidation was observed only when the resultant volume change was due to shrinkage. When the resultant volume change was positive, only uniform intragranular oxidation occurred and at the same time, extensive carburization was observed probably due to the deterioration of the surface scale caused by the deformation of the alloy substrate. A small amount of titanium, ca. 0.4%, appeared to modify the phenomena caused by aluminum additions, e.g., causing increased intergranular penetration for the 0.4% Al alloy and internal-to-external transition for the 2.1% Al alloy. External scale formation without any internal oxidation was observed for alloys containing more than 1.9% Al at 973 and 1023 K and for an alloy containing 2.1% Al and 0.4% Ti at 1073 and 1123 K. In these cases, carburization was almost completely eliminated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
For example, papers presented inNucl. Technol. 66 (1984).
R. Tanaka and T. Kondo,Nucl. Technol. 66, 75 (1984).
M. Shindo and T. Kondo,J. Japan Iron Steel Inst. 62, 66 (1976).
Y. Shida and T. Moroishi,Corros. Sci. 33, 211 (1992).
F. N. Mazandarany and G. Y. Lai,Nucl. Technol. 43, 349 (1979).
W. J. Quadakkers and H. Schuster,Nucl. Technol. 66, 383 (1984).
C. Wagner,Z. Elektrochem. 63, 772 (1959).
Y. Shida, G. C. Wood, F. H. Stott, D. P. Whittle, and B. D. Bastow,Corros. Sci. 21, 581 (1981).
F. H. Stott, Y. Shida, D. P. Whittle, G. C. Wood, and B. D. Bastow,Oxid. Met. 18, 127 (1982).
D. P. Whittle, Y. Shida, G. C. Wood, F. H. Stott, and B. D. Bastow,Phil. Mag. A 46, 931 (1982).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shida, Y., Moroishi, T. Effect of aluminum and titanium additions to Fe-21%Cr-32%Ni on the oxidation behavior in an impure helium atmosphere at high temperatures. Oxid Met 37, 327–348 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00666623
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00666623