Abstract
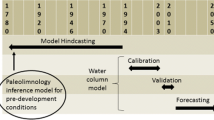
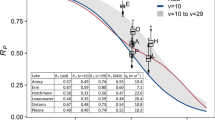
We employed three mathematical models to make quantitative estimates of the pH of 33 statistically-selected lakes in the Adirondack mountains, New York (USA) prior to the Industrial Revolution (1840). The models included 1) the MAGIC watershed acidification model, 2) a paleolimnological model of diatom-inferred pH, and 3) the MAGIC model modified to incorporate an empirically-based model of natural organic acidity. Application of approaches 2) and 3) yielded consistent estimates of pre-industrial Adirondack lakewater pH. However, when the organic acid model was not included, MAGIC calculations and diatom-inferred values showed poor agreement. MAGIC projections of lakewater pH 50 years into the future, under differing atmospheric deposition scenarios, were also sensitive to inclusion of the organic acid model. MAGIC predicted greater recovery in response to reduced deposition when organic acids were not considered. These results suggest that failure to consider the pH buffering of naturally-occurring organic acidity will often result in biased projections which overemphasize the response of lakewater pH to changes in atmospheric inputs of strong acid.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allott, T. E. H., Harriman, R. and Battarbee, R. W.: 1992,Environ. Pollut. 77, 219.
Almer, B., Dickson, W., Ekstrom, C., Hornstrom, E. and Miller, U.: 1973,Ambio 3, 30.
Baker, J. P., Bernard, D. P., Christensen, S. W. and Sale, M. J.: 1990, ‘Biological Effects of Changes in Surface Water Acid-Base Chemistry’, Report SOS/T 13, National Acid Precipitation Assessment Program, Washington, DC.
Bull, K. R.: 1992,Environ. Pollut. 77, 173.
Charles, D. F. and Smol, J. P.: 1990,Verh. Internat. Verein. Limnol. 24, 474.
Church, M. R., Thornton, K. W., Shaffer, P W., Stevens, D. L., Rochelle, B. P., Holdren, R. G., Johnson, M. G., Lee, J. J., Turner, R. S., Cassell, D. L., Lammers, D. A., Campbell, W. G., Liff, C. I., Brandt, C. C., Liegel, L. H., Bishop, G. D., Mortenson, D. C., Pierson, S. M. and Schmoyer, D. D.: 1989, ‘Direct Delayed Response Project: Future Effects of Long-Term Sulfur Deposition on Surface Water Chemistry in the Northeast and Southern Blue Ridge Province’, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Environmental Research Laboratory, EPA/600/3-89/061a-d, Washington, DC.
Cook, R. B., Rose, K. A., Brenkert, A. L. and Ryan, P. F.: 1992,Environ. Pollut. 77, 235.
Cosby, B. J., Homberger, G. M., Ryan, P. F. and Wolock, D. M.: 1989, ‘MAGIC/DDRP Final Report’, Vol. 1:Models, calibration, results, uncertainty analysis, QA/QC, Internal Report, U.S. EPA Environmental Research Laboratory-Corvallis, Corvallis, OR.
Cosby, B. J., Hornberger, G. M., Galloway, J. N. and Wright, R. F.: 1985,Water Resour. Res. 18, 51.
Cumming, B. F., Smol, J. P., Kingston, J. C., Charles, D. F., Birks, H. J. B., Camburn, K. E., Dixit, S. S., Uutala, A. J. and Selle, A. R.: 1992,Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 49, 128.
Dixit, A. S., Dixit, S. S. and Smol, J. P.: 1992,Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 62, 75.
Dixit, S. S., Dixit, A. S. and Smol, J. P.: 1991,Freshw. Biol. 26, 251.
Dixit, S. S., Dixit, A. S. and Evans, R. D.: 1987,Sci. Total Environ. 67, 75.
Dixit, S. S., Cumming, B. F., Kingston, J. C., Smol, J. P., Birks, H. J. B., Uutala, A. J., Charles, D. F. and Camburn, K. E.: 1993,J. Paleolimnology 8, 27.
Driscoll, C. T., Lehtinen, M. D. and Sullivan, T. J.: 1994,Water Resour Res. 30, 297.
Forsius, M., Kämäri, J. and Posch, M.: 1992,Environ. Pollut. 77, 185.
Hemond, H. F.: 1994, in C. E. W. Steinberg and R. F. Wright (eds.)Acidification of Freshwater Ecosystems. Implications for the Future, John Wiley, pp. 103–115.
Husar, R. B., Sullivan, T. J. and Charles. D. F.: 1991, in D. F. Charles (ed.),Acidic Deposition and Aquatic Ecosystems. Regional Case Studies, Springer-Verlag, pp. 65–82.
Jenkins, A., Whitehead, P. G., Cosby, B. J. and Birks, H. J. B.: 1990,Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. 327, 435.
Kramer, J. R. and Davies, S. S.: 1988,Environ. Sci. Technol. 22, 182.
Kretser, W., Gallagher, J. and Nicolette, J.: 1989, ‘Adirondack Lakes Study, 1984–1987’. Adirondack Lakes Survey Corp., Ray Brook, NY.
Krug, E. C. and Frink, C. R.: 1983,Science 221, 520.
Linthurst, R. A., Landers, D. H., Eilers, J. M., Brakke, D. F., Overton, W. S., Meier, E. P. and Crowe, R. E.: 1986, ‘Characteristics of Lakes in the Eastern United States’, Report EPA/600/4-86/007a, Vol. 1, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC.
APAP Aquatic Effects Working Group: 1991, ‘National Acid Precipitation Assessment Program 1990 Integrated Assessment Report’, National Acid Precipitation Assessment Program, Washington, DC.
Norton, S. A., Wright, R. F., Kahl, J. S. and Schofield, J. P.: 1992,Environ. Pollut. 77, 279.
Oliver, B. G., Thurman, E. M. and Malcolm, R. L.: 1983,Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 47, 2031.
Perdue, E. M., Reuter, J. H. and Parrish, R. S.: 1984,Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 48, 1257.
Renberg,I. and Hultberg, H.: 1992,Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 49, 65.
Sullivan, T. J., Turner, R. S., Charles, D. F., Cumming, B. F., Smol, J. P., Schofield, C. L., Driscoll, C. T., Cosby, B. J., Birks, H. J. B., Uutala, A. J., Kingston, J. C., Dixit, S. S., Bernert, J. A., Ryan, P. F. and Marmorek, D. R.: 1992,Environ. Pollut. 77, 253.
Sullivan, T. J., Bernert, J. A., Jenne, E. A., Eilers, J. M., Cosby, B. J., Charles, D. F. and Selle, A. R.: 1991, ‘Comparison of MAGIC and diatom paleolimnological model hindcasts of lakewater acidification in the Adirondack region of New York’, U.S. Department of Energy, PNL-7487/UC603, Pacific Northwest Laboratory, Richland, WA.
Wright, R. F., Cosby, B. J., Hornberger, G. M. and Galloway, J. N.: 1986,Water Air Soil Pollut. 30, 367.
Wright, R. F.: 1989,Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 46, 251.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sullivan, T.J., Cosby, B.J., Driscoll, C.T. et al. Influence of organic acids on model projections of lake acidification. Water Air Soil Pollut 91, 271–282 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00666263
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00666263