Abstract
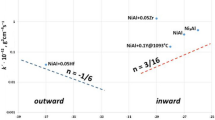
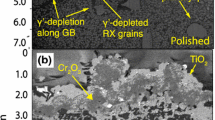
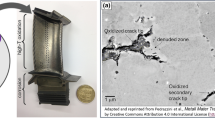
Nickel-base alloys, such as Astroloy, used for aeronautical turbine disks, are sensitive to time-dependent cracking in environments containing oxygen. The “mosaic” structure of the alloy consisting γ′ islands (200 nm average size) surrounded by the γ-phase (100 nm thick) induces complex oxidation phenomena. Various analytical approaches allow the delineation of all the steps from segregation to oxidation occurring on the surface of such a duplex structure. The protection of Astroloy by its outer oxide layer against oxygen penetration was studied also, using alternative 16O2 then 18O2 oxidation. In association with STEM studies, it is shown that the outer oxide scale is not a real barrier against oxygen penetration and that inner precipitation of chronium (+ aluminium and titanium)-enriched oxides, takes place especially in the γ structure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. S. Petit,Trans. AIME 9 (239), 1296 (1967).
C. Mons and G. Moulin, inHigh Temperature Materials for Power Engineering 1990 (Part II), E. Bacheletet al., eds. (Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, Boston, London, 1990, p. 1205.
J. Gayda and R. V. Miner,Met. Trans. A 11 (14A), 2301 (1983).
S. M. Merchant, M. R. Notis, and J. I. Goldstein,Met. Trans. A 7 (21A), 1901 (1990).
C. J. McMahon and L. F. Coffin,Met. Trans. 12 (1), 3443 (1976).
C. T. Liu and B. F. Oliver,J. Mater. Res. 2 (4), 1485 (1989).
J. E. Castle, inAnalysis of High Temperature Materials (Chap. 5), O. Van der Biest, ed. (Appl. Science Publishers, London and New York, 1983, pp. 141–172.
C. Mons, C. Lineau, C. Haut, G. Rautureau, E. Beauprez, and G. Moulin, 3rd International Symposium on High Temperature Corrosion, Les Embiez, Mai 1992, France,J. Physique (to be published).
M. P. Seah, inPractical Surface Analysis by Auger and X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (Chap. 5), D. Briggs and M. P. Seah, eds (John Wiley and Sons, New York, 1983), pp. 181–214.
N. S. McIntyre, D. G. Owen, and D. C. Zet,Appl. Surf. Sci. 2, 55 (1978).
T. L. Barr, inPractical Surface Analysis by Auger and X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (Chap. 8), D. Briggs and M. P. Seah, eds. (John Wiley and Sons, New York, 1983), pp. 283–358.
J. L. Smialek and R. Gibala,Met. Trans. 14, 2143 (1983).
K. L. Luthra and C. L. Briant,Oxid. Met. 26, 397 (1986).
V. I. Nefedov, D. Gati, B. F. Dzhurinskii, N. P. Sergushin, and Ya. V. Salyn,Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 20 (9), 1279 (1975).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moulin, G., Mons, C., Severac, C. et al. Analytical study of surface and bulk oxidation of Astroloy. Oxid Met 40, 85–108 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00665260
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00665260