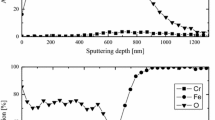
Abstract
Cyclic oxidation causes degradation of alloys used in the chemical and petrochemical industries. In this paper, the behavior of the protective oxide scales formed on Alloy 800 H and HK 40 was investigated under thermalcycling conditions with upper-hold temperatures of 900°C (Alloy 800 H) and 950°C (HK 40). The atmospheres in the tests were air, air+0.5% SO 2 and Ar-5%H 2 -50%H 2 O. Tests were accompanied by acoustic-emission measurements in order to detect scale failure in situ during the experiments. During cooling the scales were under compression which led to spalling when critical stress values were reached in the scales. The outer-spinel partial layers are more prone to spallation, and the presence of SO 2 increases the amount of acoustic-emission activity (scale damage). In the case of HK 40 the oxide scales on the as-cast surfaces showed better spallation resistance than those on the ground surfaces. Quantitative model considerations were able to describe the spallation behavior of the protective scales investigated, and critical-temperature-drop diagrams for scale failure are given. The model approach was supported by results from the acoustic-emission measurements.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Walter, M. Schütze, and A. Rahmel,Oxid. Met. 40, 37 (1993).
H. E. Evans and R. C. Lobb,Corros. Sci. 24, 209 (1984).
H. E. Evans, G. P. Mitchell, R. C. Lobb and D. R. J. Owen, A Numerical Analysis of Oxide Spallation, Report no. AGR/FPWG/P (91) 1692, Nuclear Electric PLC, Berkeley/U.K. 1991.
M. Schütze, in Proceedings of the International Symposium on Solid State Chemistry of Advanced Materials, Part B, Tokoyo, Y. Saito, B. Önay, T. Maruyama, eds. (Elsevier Science Publ., Amsterdam, 1991).
W. Christl, A. Rahmel and M. Schütze,Oxid. Met. 31, 1 (1989).
W. Christl, A. Rahmel, and M. Schütze,Oxid. Met. 31, 35 (1989).
M. Walter, Doctoral thesis, RWTH Aachen, 1991.
Mannesmann Werkstoffblätter 760 R (3.76), Hitzebeständige Stähle, Mannesmann-Röhrenwerke, Düsseldorf, 1976.
R. F. Tylecote,J. Iron Steel Inst. 196, 135 (1960).
J. Robertson and M. I. Manning,Mater. Sci. Technol. 6, 81 (1990).
Pose-Marre Brochure “Pyrotherm,” Pose-Marre Edelstahlwerk GmbH, Düsseldorf.
E. Fitzer, H. Herbst and J. Schlichting,Werkst. Korros. 24, 274 (1973).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Walter, M., Schütze, M. & Rahmel, A. Behavior of oxide scales on alloy 800 H and HK 40 during thermal cycling. Oxid Met 40, 37–63 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00665258
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00665258