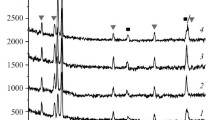
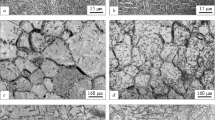
Conclusions
-
1.
The effectiveness of complex alloying was established, in which the strength of both the α and β solid solutions increases, and the difference between their strengths decreases. This leads to more even plastic deformation and more complete utilization of the strength of the α and β phases.
-
2.
The use of β stabilizing elements with distribution coefficients larger and smaller than unity is recommended in order to ensure a constant total amount of β stabilizing elements in different zones and more even decomposition of the metastable solid solution in the process of aging.
-
3.
It was found that in terms of improving the mechanical properties of Ti+3% Al+β stabilizer alloys after heat treatment the β stabilizers are arranged in the following order: Cr, Fe, Cr+Fe, Mn, V+Fe, Mo+Fe, Mo, V, Mo+Cr, Mo+V, Mo+V+Cr+Fe.
-
4.
Multicomponent alloy VT23 was developed, with σb ⩾ 145 kg/mm2 after heat treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
Additional information
Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 8, pp. 58–63, August, 1975.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khorev, A.I. Complex alloying of titanium alloys. Met Sci Heat Treat 17, 701–705 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00664322
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00664322