Abstract
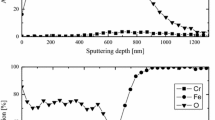
The deformation and cracking behavior of oxide scales formed in air on four heat-resistant steels and on nickel 99.6 have been studied in constant-extension-rate tests at 800°C. The strain rates in the experiments ranged between 10−6 and 10−9 s−1. Acoustic emission (AE) was used as an instrument for detecting the beginning of scale cracking. Additionally, metallographic, SEM, and micro-probe investigations were performed which supported the results from the AE measurements. The strain-to-cracking of the scales did not exceed 0.5% except when lateral growth effects in the oxide scales occurred, leading to critical strains of up to nearly 2.5%. Also the crack distribution in the scales was measured. The deformation and cracking behavior of the scales investigated could be explained by model like considerations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Rahmel, ed.,Aufbau von Oxidschichten auf Hochtemperaturwerkstoffen und ihre technische Bedeutung (Deutsche Gesellschaft für Metallkunde, Oberursel, 1983).
M. I. Manning, in Ref. 1, p. 283.
M. I. Manning, inCorrosion and Mechanical Stress at High Temperatures (Applied Science Publishers, London, 1981), p. 323.
J. Armitt, D. R. Holmes, M. I. Manning, D. B. Meadowcroft, and E. Metcalfe, The spalling of steam grown oxide from superheater and reheater tube steels. EPRI Report FP 686 (1978).
H. Riedel,Metal Sci. 16, 569 (1982).
J. C. Grosskreutz,J. Electrochem. Soc. 116, 1232 (1969).
H. E. Evans and R. C. Lobb,Corr. Sci. 24, 209 (1984).
A. G. Evans, G. B. Crumley, and R. E. Demaray,Oxid. Met. 20, 193 (1983).
G. V. Samsonow, ed.,The Oxide Handbook (IFI/Plenum, New York, 1973).
R. M. Cannon, W. H. Rhodes, and A. H. Heuer,J. Am. Ceramic Soc. 63, 46 (1980).
A. H. Heuer, N. J. Tighe, and R. M. Cannon,J. Am. Ceramic Soc. 63, 53 (1980).
R. M. Spriggs and T. Vasilos,J. Am. Ceramic Soc. 47, 47 (1964).
C. K. L. Davies,Phys. Metall. React. Fuel Elem. (Metals Society, London, 1975).
L. D. Hou, S. K. Tiku, H. Wang, and F. A. Kroeger,J. Mat. Sci. 14, 1877 (1979).
P. A. Lessing and R. S. Gordon,J. Mat. Sci. 12, 2291 (1977).
R. W. Cannon and O. D. Sherby,J. Am. Ceramic Soc. 60, 44 (1977).
B. J. Dalgleish, A. Fakhr, P. L. Pratt, and R. D. Rowlings,J. Mat. Sci. 14, 2605 (1979).
T. G. Langdon,Metal Forum 1, 59 (1978).
G. W. Groves,Proc. Br. Ceramic Soc. 15, 103 (1970).
R. v. Mises,Z. angew. Math. Mech. 8, 161 (1928).
A. G. Evans,Proc. Br. Ceramic Soc. 15, 113 (1970).
C. Gandhi and M. F. Ashby,Acta Met. 27, 1565 (1979).
B. Burton and G. L. Reynolds,J. Mat. Sci. 13, 219 (1978).
K. N. Strafford and G. Smith,Oxid. Met. 14, 119 (1980).
J. Cabrera-Cano and J. Castaing,J. Phys. Lett. 41, 119 (1980).
F. N. Rhines and J. S. Wolf,Met. Trans. 1, 1701 (1970).
M. J. Bennett and J. B. Price,Metallic Corrosion II (DECHEMA, Frankfurt, 1981), p. 1026.
K. P. Lillerud and P. Kofstad,J. Electrochem. Soc. 127, 2397 (1980).
P. Kofstad and K. P. Lillerud,J. Electrochem. Soc. 127, 2140 (1980).
M. Schütze and A. Rahmel,Corrosion Resistant Materials for Coal Conversion Systems (Applied Science Publishers, London, 1983), p. 439.
K.-H. Döhle, A. Rahmel, M. Schmidt, and M. Schütze, inRef. 3, p. 441.
J. Barbehön, K.-H. Dohle, and M. Schütze,Computer Appl. Lab. 5, 336 (1984).
F. A. Golightly, F. H. Stott, and G. C. Wood,Oxid. Met. 10, 163 (1976).
F. A. Golightly, G. C. Wood, and F. H. Stott,Oxid. Met. 14, 217 (1980).
R. G. Miner and V. Nagarajan,Oxid. Met. 16, 313 (1981).
D. Caplan and G. I. Sproule,Oxid. Met. 9, 459 (1975).
M. Welker, Diploma Thesis, University of Erlangen-Nürnberg (1983).
M. Schütze and A. Rahmel,High Temperature Corrosion (NACE, Houston, 1983), p. 421.
M. Schütze and A. Rahmel, in Ref. 1, p. 245.
C. Coddet, G. de Barros, and G. Beranger, in Ref. 3, p. 417.
G. de Barros, G. Beranger, J. F. Chretien, and C. Coddet, Action concertée Metallurgie, Université Technologie de Compiegne (1980).
R. C. Hurst and P. Hancock,Korr. 24, 33 (1973).
L. Berchtold, M. Welker, and H. G. Sockel,Werkstoffe Korr., to appear.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schütze, M. Deformation and cracking behavior of protective oxide scales on heat-resistant steels under tensile strain. Oxid Met 24, 199–232 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00664232
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00664232