Conclusions
-
1.
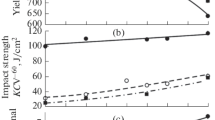
Raising the molybdenum content from 0.9 to 3.7% in austenitic steel with 19% Cr, 10% Mn, 7% Ni, and 0.30% N raises the ultimate strength to 93 kg/mm2 and the yield strength to 58 kg/mm2.
-
2.
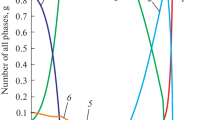
In the steel not containing molybdenum, tempering at 800°C leads to the formation of M2N and M23C6; the addition of molybdenum in amounts over 2.1% leads to preferential formation of σ phase during tempering.
-
3.
Raising the carbon content from 0.01 to 0.11% lessens the tendency to form σ phase in austenitic steel with 2.5% Mo and leads to formation of M23C6 carbide.
Similar content being viewed by others

Literature cited
A. A. Babakov et al., “Effect of nitrogen on the properties of Cr-Ni-Mn steel with Mo at low temperatures” in: Special Steels and Alloys [in Russian], Transactions of the Central Scientific-Research Institute of Ferrous Metallurgy, No. 77 (1970), pp. 113–116.
E. A. Ul'yanin et al., “Effect of carbon on mechanical properties of austenitic steel at low temperatures” Metal. i Term. Obrabotka Metal., 5, 26–27 (1966).
H. Wiegand and M. Doruk, Arch. Eisenhüttenw.,33, 559–566 (1962).
Additional information
Central Scientific-Research Institute of Ferrous Metallurgy. Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 12, pp. 27–30, December, 1974.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sorokina, N.A., Ul'yanin, E.A., Fedorova, V.I. et al. Structure and properties of stainless steel alloyed with molybdenum. Met Sci Heat Treat 16, 1027–1030 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00664042
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00664042