Conclusions
-
1.
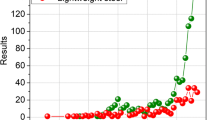
The creep resistance of 12% Cr−W−Mo−V−Nb steel is increased most effectively by alloying with zirconium, nitrogen, and aluminum due to the formation of nitrides, with the ductility remaining fairly high.
-
2.
With increasing concentrations of tungsten and molybdenum (up to 1.6%) the time to failure decreases slightly, while the addition of up to 2.0% Si, 0.7% Nb, 0.6% V, 0.4% Y, and 1.3% Ni substantially reduces the creep resistance due to the larger percentage of ferrite in the alloy, the lowering of the critical points, and weakening of atomic bonds in thecrystal lattice.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
F. F. Khimushin, Stainless Steels [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1967).
A. F. Silaev, G. P. Fedortsev-Lutikov, and M. F. Sheshenev, Chromium Heat Resistant Steels for Power Plants [in Russian], Metallurgizdat, Moscow (1963).
K. A. Lanskaya, Heat Resistant Steels [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1969).
Toshio Fugita, J. Iron Steel Inst. Japan,49, 10, 1563–1565 (1963).
Additional information
Central Scientific-Research Institute of Ferrous Metallurgy. Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 11, pp. 26–29, November, 1974.