Summary
-
1.
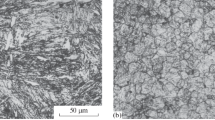
Small amounts of titanium (0.02–0.04%) may have a considerable effect on the structural transformation of normalized low-alloyed, low-carbon steel. Titanium, like boron, prevents the precipitation of the upper polygonal ferrite and promotes the supercooling of austenite to the temperature of intermediate and martensite regions. At the same time, the impact strength decreases considerably, while the strength increases.
-
2.
The critical concentration of titanium, at which its effect becomes noticeable, is determined by the presence of other alloyed elements (molybdenum, vanadium, and boron) and the austenization temperature. With increasingly complex compositions of the steel the austenization temperature (at which the stability of austenite increases) decreases.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
G. Comstock, “TASM” (1944), Vol. 33.
M. I. Kurmanov, Sh. R. Dobruskina, N. F. Leve, and A. B. Gurevich, Trudy Ukrainskogo institute metallov, No. 5 (1959).
M. I. Kurmanov, A. G. Rabinovich, and Sh. R. Dobruskina, MiTOM, No. 5 (1960).
Additional information
Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 11, pp. 42–45, November, 1965
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prokhorov, P.A. Effect of the addition of small amounts of titanium on the properties and structure of low-carbon and low-alloyed steels. Met Sci Heat Treat 7, 758–761 (1966). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00663638
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00663638