Conclusions
-
1.
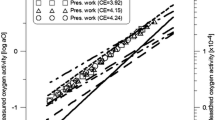
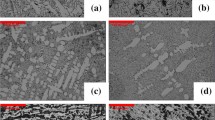
Ca, Sr, Na, and Rb are unevenly distributed in cast iron, with notable enrichment of the graphite phase in the spheroidizing element. This distribution of elements remains unchanged with different residual concentrations of these elements in the cast iron and does not induce the formation of spheroidal graphite, which is evidently due to the weak spheroidizing capacity and the relatively small residual concentrations of these elements in inoculated cast irons (in the graphite phase).
-
2.
The character of the microdistribution of the despheroidizing elements differs and is due above all to their physical and chemical properties, which determine the direction, intensity, and completeness of diffusion flows of despheroidizing elements, and consequently their enrichment of one or another of the phase and structural components.
-
3.
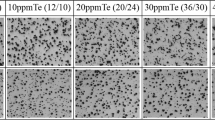
Despite the difference in the distribution of Bi, Cu, Sb, Te, Tl, Cd, In, and Ag in cast irons, the mechanism of their spheroidizing effect on graphite in high-strength magnesium cast iron is the same and is due to formation of fairly stable chemical compounds, coordination groups, etc. of the Mg-despheroidizing element system, which sharply reduces the concentration of free magnesium atoms below the minimal level required for spheroidization of graphite, and thus induces weakening of the alloy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
A. E. Krivosheev et al., "Distribution of modifying agents and their effect on the structure and properties of cast irons," Liteinoe Proizvodstvo, 2, 19–23 (1969).
A. P. Lyubchenko and M. V. Mozharov, "Liteinoe Proizvodstvo, 5, 23–25 (1969).
I. E. Lev et al., Liteinoe Proizvodstvo, 6, 23 (1971).
L. N. Balan, A. P. Lyubchenko, and M. V. Mozharov, "Microdistribution of yttrium between phase and structural components of cast irons," Liteinoe Proizvodstvo, 4, 42–44 (1970).
A. P. Lyubchenko and M. V. Mozharov, "Microdiffusion of elements during solidification of cast iron," Liteinoe Proizvodstvo, 4, 30–35 (1965).
B. I. Bruk, Autoradiographic Studies of Metals Used in Shipbuilding [in Russian], Sudostroenie, Leningrad (1966).
Z. A. Sviderskaya, M. E. Drits, and É. S. Kadaner, "Use of quantitative autoradiography to determine microheterogeneities in magnesium alloys", in: Transactions of the All-Union Scientific-Technical Conference on the Use of Radioactive and Stable Isotopes and Radiation in the National Economy and Science [in Russian], Metallurgy and Metal Science, Izd. AN SSSR, Moscow (1958), pp. 411–420.
Additional information
Khar'kov Highway Institute. Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 3, pp. 57–62, March, 1974.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Petrichenko, A.M., Mozharov, M.V., Serkhovets, S.I. et al. Distribution of alkali, alkali earth, and despheroidizing elements in cast irons. Met Sci Heat Treat 16, 256–260 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00663069
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00663069