Conclusions
-
1.
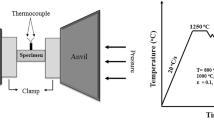
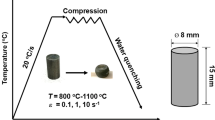
We investigated the effect of the degree and temperature of deformation and the cooling rate on the properties of three heat-resistant alloys subjected to high-temperature plastic deformation.
-
2.
It was found that high-temperature plastic deformation increases the heat resistance of the alloys at moderate temperatures (550°C) when recrystallization is completely or partially eliminated (during its initial stages).
-
3.
High-temperature plastic deformation can be successfully used for articles subjected to moderate temperatures for short periods of time.
-
4.
The fraction of samples subjected to high-temperature plastic deformation is intragranular up to higher temperatures than in samples subjected to the standard heat treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
S. T. Kishkin and A. A. Klypin. MiTOM, No. 6 (1958).
M. L. Bernshtein and Z. V. Svistunova, Stal', No. 4 (1960).
É. Perriman, Creep and Relaxation [in Russian], Metallurgizdat (1961).
D. Ya. Kagan, MiTOM, No. 1 (1960).
É. L. Demina, Dai-Tun Fu, and M. L. Bernshtein, Coll: Theory of Heat Resistance [in Russian], Izd. AN SSSR (1961).
L. A. Metashop and M. E. Blanter, MiTOM, No. 4 (1958).
Additional information
Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 1, pp. 27–30, January, 1964
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kagan, D.Y. Effect of high temperature plastic deformation on the properties of some heat-resistant alloys. Met Sci Heat Treat 6, 22–26 (1964). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00661966
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00661966