Conclusions
-
1.
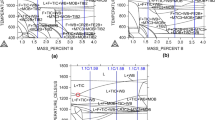
Alloying of Kh25N16GVAR steel with molybdenum increases the strength and the corrosion resistance.
-
2.
Alloying of Kh25N16GVAR steel with tungsten decreases the resistance to prolonged exposure to high temperatures.
-
3.
The addition of 2.5% Mo and 4% W increases the solubility limit of these elements in Kh25N16GTAR steel, and this leads to the formation of intermetallic phases and to embrittlement of the steels heated to 700-1000°C.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
F.F. Khimushin, Stainless Steels [in Russian], Metallurgizdat (1963).
N.F. Lashko and N. I. Eremin, Phase Analysis and Structure of Austenitic Steels [in Russian], Moscow, Mashgiz (1957).
Additional information
Elektrostal' Plant Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 1, pp. 17-19, January, 1966
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boyarinova, A.P., Savel'eva, T.S. & Dubrovina, A.N. Effect of molybdenum and tungsten on the properties of Kh25N16G7AR steel. Met Sci Heat Treat 8, 18–20 (1966). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00660156
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00660156