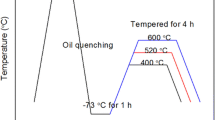
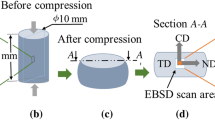
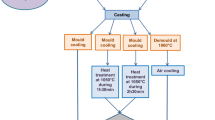
Conclusions
-
1.
The susceptibility of steel 000Kh16N15M3 to intercrystalline corrosion corresponds to the formation of an almost continuous network of etched grain boundaries and carbides in the form of dendrites that are visible by transmission electron microscopy.
-
2.
The disappearance of susceptibility to intercrystalline corrosion corresponds to the formation of carbides with various geometric shapes that are not transparent to the electron beam and a discontinuous network of carbides in the grain boundaries.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
A. N. Pilyankevich, Practice of Electron Microscopy [in Russian], Mashgiz, Moscow-Kiev (1961).
R. Stickler and A. Vinkier, Mem. Scient. Rev. Metallurgie.,60, No. 78 (1963).
A. P. Gulyaev and K. E. Miroshinkova, Metal. i Term. Obrabotka Metal., No. 2 (1965).
A. A. Babakov, T. V. Svistunova, and N. F. Chermenskaya, Metal. i Term. Obrabotka Metal., No. 12 (1965).
H. Heatwell, Coll: Corrosion of Metals [Russian translation], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1964).
Additional information
TsNIICHERMET. Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka metallov, No. 3, pp. 38–40, March, 1969.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fel'dgandler, É.G., Savkina, L.Y. Intercrystalline corrosion and structure of steel 000Kh16N15M3. Met Sci Heat Treat 11, 203–205 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00658733
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00658733