Abstract
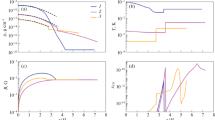
We describe the construction and main properties of stationary accretion discs that are supposed to produce the high luminosities of Active Galactic Nuclei. It is found that for most parameter combinations the discs are geometrically thin everywhere. However, for high accretion rates and/or low local energy generation rates they may get thick close to the central object. The distributions of the temperature, the gas pressure and the vertical optical depth are characterized by steep gradients close to the surface and very flat stratifications in the inner parts. The ratio of the radiation pressure to the gas pressure varies over several orders of magnitude within a disc. The emergent fluxes can be well approximated by power laws in a wide wavelength range but turn over in the middle or extreme UV range. It is argued that this range is best suited for spectral diagnosis from the continuum.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Engeln-Müllges, G., and Reutter, F.: 1988,Formelsammlung zur Numerischen Mathematik, Wissenschaftsverlag: Mannheim.
Frank, J., King, A.R., and Raine, D.J.: 1985,Accretion Power in Astrophysics, Cambridge University Press: Cambridge.
Kahaner, D., Moler, C., and Nash, S: 1989,Numerical Methodes and Software, Prentice-Hall: London.
Rees, M.: 1984,Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 22, 471.
Shaviv, G. and Wehrse, R.: 1991,Astron. Astroph. 251, 117.
Shaviv, G. and Wehrse, R.: 1992, in: Wheeler, C.J. (ed.),Accretion Discs in Compact Stellar Systems, World Scientific: Singapore.
Störzer, H.: 1992,Astron. Astroph., submitted.
Sun, W.H., and Malkan, M.A.: 1989,Astroph. J. 346, 68.
Terlevich, R.: 1989, in: Fabbiano, G., Gallagher, J.S., and Renzini, A. (eds.),Windows in Galaxies, Kluwer: Dordrecht.
Wehrse, R. and Shaviv, G.: 1991, in: Bertout, C., Collin, S., Lasota, J.-P., and Tran Thanh Van, J. (eds).,Structure and Emission Properties of Accretion Disks, Ed. Frontières: Paris.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wehrse, R., Störzer, H. & Shaviv, G. The vertical structure and radiation fields of accretion discs in the centres of AGNs. Astrophys Space Sci 205, 163–169 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00657972
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00657972