Conclusions
-
1.
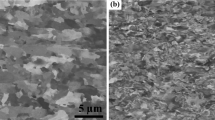
The increase of grain size during welding depends on the cooling rate and on the time the metal remains at temperatures above the α→γ transformation temperature.
-
2.
Cooling from α→γ transformation temperatures at a low rate leads to an increase in the amount of retained austenite and some reduction of hardness in the heat-affected zone.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
M. Kh. Shorshorov, Metal Science of Welding Steels and Titanium Alloys [in Russian], Nauka, Moscow (1965).
S. A. Saltykov, Stereometric Metallography [in Russian], Metallurgizdat, Moscow (1958).
M. D. Perkas, "High-strength maraging steels", Metal. i Term. Obrabotka Metal., 6 (1968).
A. P. Gulyaev and N. I. Karchevskaya, "Martensitic transformation in alloy N18K8M3T", Fiz. Metal. Metalloved.,23, 1 (1967).
Additional information
A. A. Baikov Institute of Metallurgy. Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 11, pp. 62–63, November, 1973.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shorshorov, M.K., Antipov, V.I., Kudinov, E.D. et al. Effect of the thermal cycle in welding on the structure and phase composition of the heat-affected zone in maraging steel. Met Sci Heat Treat 15, 991–992 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00656690
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00656690