Abstract
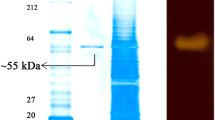
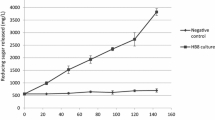
Maximum production of extracellular α-amylase activity inHalobacterium halobium was at 40°C in a medium containing 25% (w/v) NaCl, 1% (w/v) soluble starch and 1% (w/v) peptone, in presence of 0.1mm ZnSO4 after 5 days in shaking cultures. The amylase had optimal activity at pH 6.5 in the presence of 1 to 3% (w/v) NaCl at 53°C.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Danson, M.J. 1988 Archaebacteria: the comparative enzymology of their central metabolic pathways.Advances in Microbial Physiology 29, 165–231.
Denault, L.J. & Underkofler, L.A. 1963 Conversion of starch by microbial enzymes for production of syrups and sugars.Cereal Chemistry 40, 618–629.
Eisenberg, H. & Wachtel, E.J. 1987 Structural studies of halophilic proteins, ribosomes and organelles of bacteria adapted to extreme salt concentrations.Annual Reviews in Biophysics and Biophysiological Chemistry 16, 69–92.
Good, W.A. & Hartman, P.A. 1970 Properties of the amylase fromHalobacterium halobium.Journal of Bacteriology 104, 601–603.
Hough, D.W. & Danson, M.J. 1989 Archaebacteria: ancient organisms with commercial potential.Letters in Applied Microbiology 9, 33–39.
Komaki, T. 1956 Industrial applications of amylase.Denpum Kogyo Gakkaishi 4, 1–8.
Kushner, D.J. 1985 The Halobacteriaceae. In:The Bacteria Vol. 8, eds. Woese, C.R. & Wolf, R.S.; pp. 171–214. London: Academic Press.
Miller, G.L. 1959 Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugars.Analytical Chemistry 31, 426–428.
Oesterhelt, D. & Krippahl, G. 1983 Phototrophic growth of Halobacteria and its use for isolation of photosynthetically deficient mutants.Annals of Microbiology 134, 137–150.
Zaccai, G. & Eisenberg, H. 1990 Halophilic proteins and the influence of solvent on protein stabilization.Trends in Biochemical Sciences 15, 333–337.
Additional information
S. Patel, N. Jain and D. Madamwar are with the Post Graduate Department of Biosciences, Sadar Patel University, Vallabh Vidyanagar-388120, India.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patel, S., Jain, N. & Madamwar, D. Production of α-amylase fromHalobacterium halobium . World J Microbiol Biotechnol 9, 25–28 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00656510
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00656510