Conclusions
-
1.
In the as-received state (air hardened from 1100°C (2010°F) and further heated at 700°C (1290°F) for 20 min.), the steel examined, which came from production heats, did not suffer intercrystalline decay in any of the solutions used.
-
2.
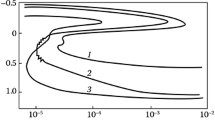
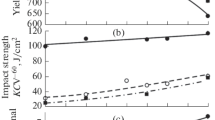
Whatever the test method (methods A, AM, and C), the higher the hardening temperature, the more susceptible this steel becomes to intercrystalline breakdown after being subjected to 120 min of further heating.
-
3.
That the steel is most susceptible to intercrystalline decay after quenching from the higher temperature is due to the solution in the austenite of a portion of the titanium carbides, and to the subsequent loss of chromium by the boundary regions during tempering.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. V. Skorchelleti and V. A. Titova,Zhurnal Prikl. Kim., Vol. 16, 1943, (1).
E. Brauns and G. Pier,Stahl und Eisen, Vol. 75, 1955, (9), pp 579–586. [Available as HB translation No. 3662].
N. P. Zhetvin et al., The Descaling of Metals [B], Metallurgizdat Press, 1957.
Additional information
Central Research Institute For Ferrous Metallurgy
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zotova, E.V. Susceptibility of high chrome-nickel-molybdenum-copper steel 0Kh23N28M3D3 (EI943) to intercrystalline corrosion. Met Sci Heat Treat 2, 21–22 (1962). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00655584
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00655584