Abstract
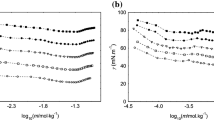
In the case of cationic polystyrene latex, the adsorption of anionic surfactants involves a strong electrostatic interaction between both the particle and the surfactant, which may affect the conformation of the surfactant molecules adsorbed onto the latex-particle surface. The adsorption isotherms showed that adsorption takes place according to two different mechanisms. First, the initial adsorption of the anionic surfactant molecules on cationic polystyrene surface would be due to the attractive electrostatic interaction between both ionic groups, laying the alkyl-chains of surfactant molecules flat on the surface as a consequence of the hydrophobic interaction between these chains and the polystyrene particle surface, which is predominantly hydrophobic. Second, at higher surface coverage the adsorbed surfactant molecules may move into a partly vertical orientation with some head groups facing the solution. According to this second mechanism the hydrophobic interactions of hydrocarbon chains play an important role in the adsorption of surfactant molecules at high surface coverage. This would account for the very high negative mobilities obtained at surfactant concentration higher than 5×10−7 M. Under high surface-coverage conditions, some electrophoretic mobility measurements were performed at different ionic strength. The appearance of a maximum in the mobility-ionic strength curves seems to depend upon alkyl-chain length. Also the effects of temperature and pH on mobilities of anionic surfactant-cationic latex particles have been studied. The mobility of the particles covered by alkyl-sulphonate surfactants varied with the pH in a similar manner as it does with negatively charged sulphated latex particles, which indicates that the surfactant now controls the surface charge and the hydrophobic-hydrophilic character of the surface.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonekamp BC, Hidalgo-Alvarez R, de las Nieves FJ, Bijsterbosch BH (1987) J Colloid Interface Sci 118:366
Zsom RLJ (1986) J Colloid Interface Sci 111:434
Vijayendran BR (1979) J Appl Polymer Sci 23:733
Connor P, Ottewill RH (1971) J Colloid Interface Sci 37:642
Goodwin JW, Ottewill RH, Pelton R (1979) Colloid Polym Sci 257:61
Hidalgo-Alvarez R, de las Nieves FJ, van der Linde AJ, Bijsterbosch BH (1986) Colloids Surfaces 21:259
Cañete F, Rios A, Luque de Castro MD, Valcarcel M (1988) Analytical Chem 60:2354
Perea-Carpio R, Gonzalez-Caballero F, Bruque JM, Pardo G (1983) J Colloid Interface Sci 95:513
Fuerstenau DW (1956) J Phys Chem 60:981
Van den Hoven ThJJ (1984) Ph D dissertation. University of Wageningen
Ottewill RH, Rastogi MC, Watanabe H (1960) Trans Faraday Soc 56:854
Somasundaran P, Healy TW, Fuerstenau DW (1964) J Phys Chem 68:3562
Midmore BR, Hunter RJ (1988) J Colloid Interface Sci 122:521
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dedicated to the memory of Dr. Safwan Al-Khouri Ibrahim
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
González, F.G., Vilchez, M.A.C. & Hidalgo-Alvarez, R. Adsorption of anionic surfactants on positively charged polystyrene particles II. Colloid Polym Sci 269, 406–411 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00654587
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00654587