Conclusions
-
1.
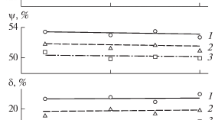
The increased resistance of steels to corrosion cracking is manifest in the longer induction period and lower crack propagation rate.
-
2.
Susceptibility to corrosion cracking depends essentially on the heat treatment. The structure with the highest thermodynamic stability has the highest resistance.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
I. A. Oding et al., Theory of Creep and Long-term Strength of Metals [in Russian], Metallurgizdat, Moscow (1959).
Additional information
Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 7, pp. 66–69, July, 1968.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zakharov, Y.V., Lupakov, I.S. Effect of heat treatment on time before failure of chromium steels in corrosive media. Met Sci Heat Treat 10, 561–563 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00654370
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00654370