Abstract
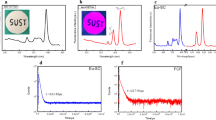
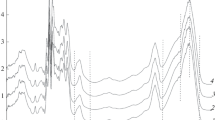
Fluorescent whitening agents (FWA) are used to improve the whiteness of cellulose fabrics. It is well known but not completely understood that the fluorescence decreases (chemical and physical mechanisms of distinguishing) above a certain FWA concentrationc crit. This reduction of fluorescence correlates very well with the alteration of the adsorption process studied by calorimetry and zeta potential measurements. The results obtained by these methods indicate that the adsorption mechanism is different at concentrations below and abovec crit. The reduction of the intensity of fluorescence, the degree of whiteness and the zeta potential are caused by the adsorption of a second layer of fluorescent whitening agents. This second layer reduces the zeta potential due to a shielding effect and reduces the whiteness and fluorescence by a bathochromic shift of the reflection curves. The final effect is a reduction of the total reflection.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lewin M, Sello SB (1984) In: Chemical Processing of Fibers and Fabrics, Fundamentals and Preparation. Marcel Dekker, Inc, New York, Basel, pp 258–261, 265–267
Anliker R, Müller G (1975) In: Fluorescent Whitening Agents. Georg Thieme Publishers, Stuttgart, pp 24–30
Stana K (1992) Belina in fluorescenca ekolosko neoporecno beljenega celuloznega vlakna, Magistrsko delo, Tehniska fakulteta Maribor, p 46–67
Èunko R (1985) Textiltechnik 35(4): 206–211
Siegrist AE, Hefti H, Meyer HR, Schmidt E (1987) Rev Prog Coloration 17:39–51
Gouy G (1910) J Phys Chem 9:457–462;
Stern O (1924) Z Elektrochemie 30: 508–516; Graham D (1947) Chem Rev 41:441–501; Chapmann DL (1913) Phil Mag 25:475
Schurz J, Erk G, Schempp W, Ribitsch V (1990) J Macromol Sci Chem A 27:1673–1692
Ribitsch V, Jacobasch HJ, Boerner M (1991) In: Advances in Measurement and Control of Colloidal Processes. Butterworth-Heinemann, pp 354–365
Fairbrother F, Mastin H (1924) J Chem Soc 75:2318–2323
Bronswijk JP, de Loo M, van Loo W (1993) Heat measurement with the Thermal Activity Monitor, reprinted from World Cement
Jacobasch HJ, Bauböck G, Schurz J (1985) Colloid Polym Sci 263:3–24
Espinosa-Jimenez, Gonzales Caballero F (1991) Cellulose Chem Technol 65–77
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stana, K.K., Pohar, C. & Ribitsch, V. Adsorption of whitening agents on cellulose fibers — Monitored by streaming potential measurements, calorimetry and fluorescence. Colloid Polym Sci 273, 1174–1178 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00653086
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00653086