Abstract
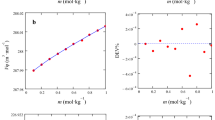
The apparent molar volumes Vϕ and heat capacities C p,ϕ of NaCl, LiCl, NaF, KI, NaBPh4 and Ph4PCl have been determined in solutions of H2O containing up to 40 mass% t-butyl alcohol (TBA) by flow densitometry and flow microcalorimetry. Combination of these results with literature data allows calculation of Vϕ and C p,ϕ for 16 ions in these mixtures using the assumption that ΔtXφ(Ph4P+) = ΔtXφ(BPh −4 ) where X=V or C p and ΔtXφ is the change in Xϕ for a species on transfer from H2O to TBA-H2O mixtures. These are the first reported single ion values for C p,ϕ in a mixed solvent. While whole electrolyte volumes and heat capacities show relatively smooth changes with solvent composition, ΔtXφ(ion) exhibit two well-developed extrema at around 10 and 25 mass% TBA. The shape of the ΔtXφ(ion) curves shows considerable uniformity among the alkali metal cations and the halide ions but the extrema become more pronounced with increasing size among the tetraalkylammonium ions. These extrema are analogous to those observed in aqueous organic mixtures of surfactants and are probably indicative of microphase transitions in these strongly interacting solvent mixtures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. E. Desnoyers and C. Jolicoeur, inComprehensive Treatise of Electrochemistry, B. E. Conway, J. O. Bockris, and E. Yeager, eds., (Plenum, NY, 1983), Vol. 5, Chap. 1.
J. E. Desnoyers, G. Perron, and A. H. Roux, inSurfactant Solutions — New Methods of Investigation, R. Zana, ed., (Marcel Dekker, NY, 1987), Chap. 1.
J.-P. E. Grolier, G. Roux-Desgranges, and A. H. Roux,Fluid Phase Equil. 30, 157 (1986).
L. G. Hepler, Z. S. Kooner, G. Roux-Desgranges, and J.-P. E. Grolier,J. Solution Chem. 14, 579 (1985).
M. H. Abraham and Y. Marcus,J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. I 82, 3255 (1986).
M. H. Abraham, Y. Marcus, and K. G. Lawrence,J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. I,84, 175 (1988).
F. J. Millero,Chem. Rev. 71, 147 (1971).
R. Zana, J. E. Desnoyers, G. Perron, R. L. Kay, and K. S. Lee,J. Phys. Chem. 86, 3996 (1982) and references cited therein.
M. J. Mastroianni and C. M. Criss,J. Chem. Thermodyn. 4, 321 (1972).
A. J. Pasztor and C. M. Criss,J. Solution Chem. 7, 27 (1978).
R. Zana, G. Perron, and J. E. Desnoyers,J. Solution Chem. 8, 729 (1979).
Y. Marcus,Ion Solvation (Wiley, New York, 1985).
O. Popovych and R. Tomkins,Non Aqueous Solution Chemistry (Wiley-Interscience, New York, 1981).
L. Avedikian, G. Perron, and J. E. Desnoyers,J. Solution Chem. 4, 331 (1975).
F. Franks and J. E. Desnoyers,Water Sci. Rev. 1, 171 (1985).
E. Wilhelm, J.-P. E. Grolier, and M. H. Karbalai Ghassemi,Ber. Bunsenges Phys. Chem. 81, 925 (1977).
J.-P. E. Grolier, E. Wilhelm, and M. H. Hamedi,Ber. Bunsenges Phys. Chem. 82, 1282 (1978).
J. E. Desnoyers, O. Kiyohara, G. Perron, and L. Avedikian,Adv. Chem. Ser. 155, 274 (1976).
A. H. Roux, D. Hétu, G. Perron, and J. E. Desnoyers,J. Solution Chem. 13, 1 (1984).
J. E. Desnoyers, G. Caron, R. De Lisi, D. Roberts, A. Roux, and G. Perron,J. Phys. Chem. 87, 1397 (1983).
R. N. French and C. M. Criss,J. Solution Chem. 11, 625 (1982).
V. Gutmann,The Donor-Acceptor Approach to Molecular Interactions (Plenum, New York, 1978).
B. E. Conway,Ionic Hydration in Chemistry and Biophysics (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1981).
K. Bose, A. K. Das, and K. K. Kundu,J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. I 71 1838 (1975).
C. F. Wells,J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. I 72, 601 (1976).
J. E. Desnoyers, G. Perron, L. Avedikian, and J.-P. Morel,J. Solution Chem. 5, 631 (1976).
L. G. Hepler,J. Phys. Chem. 61, 1426 (1957).
F. Kawaizumi and R. Zana,J. Phys. Chem. 78, 1099 (1974).
U. Mayer, inIons and Molecules in Solution, N. Tanaka, H. Ohtaki, R. Tamamushi, eds., (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1982), p. 219.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hefter, G.T., Grolier, J.P.E. & Roux, A.H. Apparent molar heat capacities and volumes of electrolytes and ions int-butanol-water mixtures. J Solution Chem 18, 229–248 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00652986
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00652986