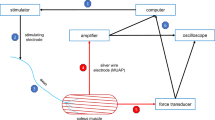
Abstract
Experiments were carried out to investigate the changes which occur in the energy production of cross reinnervated fast and slow twitch skeletal muscles. Rat soleus (SOL) and extensor digitorum longus (EDL) muscles were used in myothermic experiments. It was found that the energy production of cross reinnervated skeletal muscle is largely determined by the source of the nervous innervation; as are the dynamic and histological properties of mammalian skeletal muscle. There was an increase in the energy production of crossed soleus muscle and a concomitant reduction in the energy production of crossed EDL. The changes observed correlated well with the measured changes in the force-velocity properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amphlett GW, Perry SV, Syska H, Brown MD, Vrbova G (1975) Cross-innervation and regulatory protein system of rabbit soleus muscle. Nature 257:602–604
Ariano MA, Armstrong RB, Edgerton VR (1973) Hindlimb muscle fibre population of five mammals. J Histochem Cytochem 21:51–55
Bárány M, Close RI (1971) The transformation of myosin in cross-reinnervated rat muscles. J Physiol (Lond) 213:455–474
Briggs FN, Poland JL, Solaro RJ (1977) Relative capabilities of sarcoplasmic reticulum in fast and slow skeletal muscles. J Physiol (Lond) 266:587–594
Buller AJ, Mommaerts WFHM, Seraydarian K (1969) Enzymic properties of myosin in fast and slow twitch muscles of the cat following cross-reinnervation. J Physiol (Lond) 205:281–297
Chapman JB, Gibbs CL (1972) An energic model of muscle contraction. Biophys J 12:227–235
Close R (1964) Dynamic properties of fast and slow skeletal muscles of the rat during development. J Physiol (Lond) 173:74–95
Close R (1965) Effects of cross-union of motor nerves on fast and slow skeletal muscles. Nature 206:831–832
Close R (1969) Dynamic properties of fast and slow skeletal muscles of the rat after nerve cross-union. J Physiol (Lond) 204:331–346
Close R, Hoh JFY (1969) Post tetanic potentiation of twitch contraction of cross-innervated rat fast and slow muscles. Nature 221:179–181
Crow MT, Kushmerick MJ (1982) Chemical energetics of slow- and fast-twitch muscles of the mouse. J Gen Physiol 79:147–166
Davey DF (1975) Morphometric analysis of rat fast and slow twitch muscles. Proc Aust Physiol Pharmacol Soc 6:45–46
Dubowitz V (1967) Cross reinnervated mammalian skeletal muscle. Histochemical, physiological and biochemical observations. J Physiol (Lond) 193:481–496
Gallego R, Kuno M, Nunez R, Snider WD (1979) Dependence of motoneurone properties on the length of immobilized muscles. J Physiol (Lond) 291:179–189
Gibbs CL (1978) Cardiac energetics. Physiol Rev 58:174–254
Gibbs CL, Gibson WR (1972) Energy production of rat soleus muscle. Am J Physiol 223:864–871
Gibbs CL, Ricchiuti NV, Mommaerts WFHM (1966) Activation heat in frog sartorius muscle. J Gen Physiol 49:517–535
Hasselbach W, Makinose M (1962) ATP and active transport Biochem Biophys Res Commun 7:132–136
Hill AV (1938) The heat of shortening and the dynamic constants of muscle. Proc Roy Soc (Lond) B 126:136–195
Hill AV (1964) In: Trials and trails in physiology, chapter 6. Arnold, London
Hoffman WM (1976) Oxygen consumption of human and rodent striated muscle in vitro. Am J Physiol 230:34–40
Hoh JFY (1975) Neural regulation of mammalian fast and slow myosins: An electrophoretic analysis. Biochemistry 14:742–747
Homsher E, Mommaerts WFHM, Ricchiuti NV, Wallner A (1972) Activation heat, activation metabolism and tension related to heat in frog semitendinosus muscle. J Physiol (Lond) 220:601–625
Jewell BR, Kretzschmar M, Woledge RC (1967) Length and tension transducers. J Physiol (Lond) 191:10P-12P
Jolesz F, Sreter FA (1981) Development, innervation and activity-pattern induced changes in skeletal muscle. Ann Rev Physiol 43:531–552
Loiselle DS, Wendt IR, Hoh JFY (1982) Energetic consequences of thyroid-modulated shifts in ventricular isomyosin distribution in the rat. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 3:5–23
Luff AR, Atwood, HL (1971) Changes in the sarcoplasmic reticulum and transverse tubular system of the fast and slow skeletal muscles of the mouse during post natal development. J Cell Biol 51:369–383
Margreth A, Salviati G, Carraro U (1973) Neural control of the activity of the calcium transport system of the SR of the rat skeletal muscle. Nature 214:285–286
Rall JA (1979) Effect of temperature on tension, tension-dependent heat and activation heat in twitches of frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol (Lond) 291:265–275
Ramirez BU, Pette D (1974) Effects of long term electrical stimulation on sarcoplasmic reticulum of fast rabbit muscle. FEBS Lett 49:188–190
Sandberg JA, Carlson FD (1966) The length dependence of phosphorylcreatine hydrolysis during an isometric tetanus. Biochem Z 345:212–231
Smith ICH (1972) Energetics of activation heat in frog and toad muscle. J Physiol (Lond) 220:583–599
Wendt IR (1974) A comparative study of the energetics of mammalian fast and slow twitch muscles Ph D Thesis, Monash University
Wendt IR, Gibbs CL (1973) Energy production of rat extensor digitorum longus muscles. Am J Physiol 224:1081–1086
Wendt IR, Gibbs CL (1974) Energy production of mammalian fast and slow twitch muscles during development. Am J Physiol 226:642–647
Wilkie DR (1968) Heat work and phosphorylcreatine breakdown in muscle. J Physiol (London) 195:157–183
Woledge RC (1968) The energetics of tortoise muscle. J Physiol (Lond) 197:685–707
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ziccone, S., Gibbs, C. Effects of cross reinnervation on the energetics of rat skeletal muscle. Pflugers Arch. 399, 297–301 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00652756
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00652756