Abstract
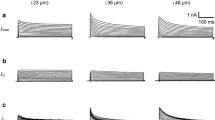
1. The voltage clamp technique was used to study the effects of dendrotoxin (DTX) on outward potassium currents in internally perfused dorsal root ganglion neurones of guinea-pig. Sodium currents were eliminated by tetrodotoxin (TTX, 2 μmol/l), calcium currents and calcium-activated potassium conductances were abolished by intracellular perfusion of cells with KF. 2. Depolarizing voltage shifts from a holding potential of −90 mV yielded a fast transient outward current (I fK ) and a delayed non-inactivating outward current (I K/s). These currents could be separated by shifting the membrane potential to −50 mV, whereI fK was almost completely inactivated. 3. DTX, at concentrations of 0.14–1.4 nmol/l selectively reduced a portion of the non-inactivating potassium current, leaving the transient outward current unaffected. Once manifested, the action of DTX could not be reversed by washing. 4. The I–V characteristic of the current blocked by DTX is almost linear and quite different from the one of the ‘DTX-resistant’ portion ofI sK , which shows a non-linear I–V curve. 5. Tetraethylammonium (TEA, 30 mmol/l) strongly reducedI fK andI sK . However, subsequent application of DTX was still able to further reduceI sK . 6. 3,4-diaminopyridine (3,4-DAP, 500 μmol/l) unselectively reducedI fK and a portion ofI sK . The remainder of the latter could not further be reduced by DTX, suggesting a similar action of the two blockers on non-inactivating potassium currents. 7. From the results presented, it is suggested that dendrotoxin selectively blocks a non-inactivating subtype of potassium channel.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bkaily G, Sperelakis N, Renaud JF, Payet MD (1985) Apamin, a highly specific Ca2+ blocking agent in heart muscle. Am J Physiol 248:H961-H965
Carbone E, Wanke E, Prestipino G, Possani LD, Maelicke A (1982) Selective blockage of voltage-dependent K+-channels by a novel scorpion toxin. Nature 296:90–91
Dolly JO, Halliwell JV, Black JD, Williams RS, Pelchen-Matthews A, Breeze AL, Mahraban F, Othman IB, Black AR (1984) Botulinum neurotoxin and dendrotoxin as probes for studies on transmitter release. J Physiol (Paris) 79:280–303
Harvey AL, Gage PW (1981) Increase of evoked release of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction by a fraction from the venom of the eastern green mamba snake (Dendroaspis angusticeps). Toxicon 19:373–381
Harvey AL, Karlsson E (1980) Dendrotoxin from the venom of the green mamba, Dendroaspis angusticeps. A neurotoxin that enhances acetylcholine release of neuromuscular junctions. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 312:1–6
Harvey AL, Karlsson E (1982) Protease inhibitor homologues from mamba venoms: facilitation of acetylcholine release and interactions with prejunctional blocking toxins. Br J Pharmacol 77:153–161
Kirsch GE, Narahashi T (1978) 3,4-Diaminopyridine: a potent new potassium channel blocker. Biophys J 22:507–512
Kostyuk PG, Veselovsky NS, Tsyndrenko AY (1981a) Ionic currents in the somatic membrane of rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. I. Sodium currents. Neurosci 6:2423–2430
Kostyuk PG, Veselovsky NS, Fedulova SA, Tsyndrenko AY (1981b) Ionic currents in the somatic membrane of rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. III. Potassium currents. Neurosci 6:2439–2444
Pennefather P, Lancaster B, Adams PR, Nicoll RA (1985) Two distinct Ca-dependent K currents in bullfrog sympathetic ganglion cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:3040–3044
Rogawski MA (1985) The A-current: how ubiquitous a feature of excitable cells is it? Trends in Neurosci 83:214–219
Romey G, Hugues M, Schmidt-Antomarchi H, Lazdunski M (1984) Apamin: a specific toxin to study a class of Ca2+-dependent K+ channels. J Physiol (Paris) 79:259–264
Schwarz JR, Vogel W (1971) Potassium inactivation in single myelinated nerve fibres ofXenopus laevis. Pflügers Arch 330:61–73
Weller U, Bernhardt U, Siemen D, Dreyer F, Vogel W, Habermann E (1985) Electrophysiological and neurobiochemical evidence for the blockade of a potassium channel by dendrotoxin. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 330:77–83
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This is part of the thesis of R.P. to be presented to the Fachbereich Biologie, Justus-Liebig-Universität Gießen
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Penner, R., Petersen, M., Pierau, F.K. et al. Dendrotoxin: a selective blocker of a non-inactivating potassium current in guinea-pig dorsal root ganglion neurones. Pflugers Arch. 407, 365–369 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00652619
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00652619