Conclusions
-
1.
Sheets of technically pure commercial VT1 titanium as delivered have a small grained structure with the grain size corresponding to grade 7-6.
-
2.
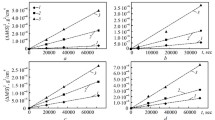
Heating in air at 650°C leads to a considerable increase in the surface hardness of VT1 titanium. The microhardness on the surface of the sheet is H 405; it is H 196 in the center.
-
3.
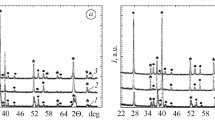
Heating of VT1 titanium and the OT4 alloy for 2 h at 750–850°C leads to the saturation of the surface layer with gases and, as the result, a gray oxide film 15 microns thick is formed with a hardness of H 727 in the case of VT1 titanium and H 1030 in the case of the OT4 alloy.
-
4.
Heating above the temperature of allotropic transformation (from 950 to 1050°C) leads to the formation of a white oxide film with a higher hardness on the surface of VT1 titanium and the OT4 alloy: H 1079 in the case of titanium and H 1300–1410 in the case of the OT4 alloy. Under the oxide layer there is a very hard diffusion layer. The depth of penetration of oxygen into the metal depends on the temperature and heating time.
Similar content being viewed by others
Additional information
Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 2, pp. 51–55, February, 1966
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akshentseva, A.P., Shumratova, G.N. Influence of heat treatment on the structure and properties of VT1 titanium and the OT4 alloy. Met Sci Heat Treat 8, 147–150 (1966). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00652611
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00652611