Conclusions
-
1.
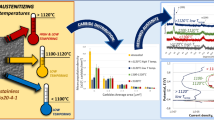
The parameters of induction heating (temperature, heating rate, and duration of isothermal heating) have a significant influence on the fine structure of Kh18N9T stainless steel.
-
2.
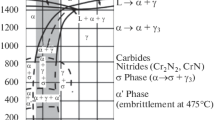
Isothermal heating at 1100°C favors the dissolution of chromium carbides and increases the resistance of Kh18N9T steel to intercrystalline corrosion.
-
3.
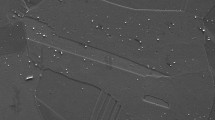
There is a relationship between the susceptibility to intercrystalline corrosion of Kh18N9T steel and the distribution and amount of chronium carbides resulting from different conditions of induction heating: The steel is susceptible to intercrystalline corrosion when there are chronium carbides situated in lines along the grain boundaries or accumulated in separate areas.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
K. Z. Shepelyakovskii, MiTOM (1963), No. 6.
Additional information
All-Union Correspondance Polytechnical Institute Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 2, pp. 21–25, February, 1966
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pogodina-Alekseeva, K.M., Loshnevskaya, A.A. Influence of induction heating on the fine structure of austenitic stainless steel. Met Sci Heat Treat 8, 113–116 (1966). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00652600
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00652600