Conclusions
-
1.
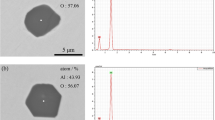
Modification of St. 3 steel with rare earth metals of the Ce subgroup changes the character of the crystallization of the ingot. In the outer area there are no columnar dendrites and the structure is more uniform. Small inclusions of sulfur are distributed along the axes of dendrites, while large inclusions are located in the interaxial space.
-
2.
The addition of 0.20% Ce displaces sulfur from the boundaries of the grains, which increases the ductility and the plasticity of the steel at high temperatures. When the concentration of cerium is high (0.4% Ce) then the modification of the steel leads to the precipitation of sulfides along the grain boundaries, which has a negative effect on the properties of the steel.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 2, pp. 18–20, February, 1966
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Popova, N.N., Sandler, N.I., Kovalev, G.N. et al. Influence of rare earth elements on the crystallization of carbon steel. Met Sci Heat Treat 8, 110–112 (1966). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00652599
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00652599