Abstract
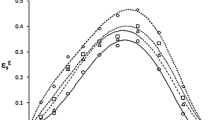
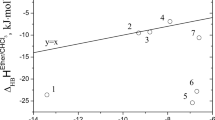
In the ideal associated solution model, activity coefficients of all species (labelled A, B, and AB here) at equilibrium are taken to be unity at all compositions and temperatures. We have applied this model to an analysis of thermodynamic properties (vapor pressures, excess enthalpies, partial molar enthalpies of solution, excess heat capacities, and excess volumes) of the chloroform+benzene system in terms of K, ΔHθ, ΔC θp , and ΔVθ for the equilibrium represented by A+B=AB. It is demonstrated that there is reasonably good consistency between this simple model and all of the thermodynamic data, which shows that the model is realistic enough to be useful in assessing the properties of the not-very-stable AB complex in the chloroform+benzene system. New thermal (partial molar enthalpies of solution and excess heat capacities) and volumetric properties of the chloroform+benzene system have been measured, with results presented here.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. G. Hepler, Z. S. Kooner, G. Roux-Desgranges, and J.-P. E. Grolier,J. Solution Chem. 14, 579 (1985).
L. W. Reeves and W. G. SchneiderCan. J. Chem. 35, 251 (1957).
C. J. Creswell and A. L. Allred,J. Phys. Chem. 66, 1469 (1962).
W. T. Huntress, Jr.,J. Phys. Chem. 73, 103 (1969).
W. C. Lin and S.-J. Tsay,J. Phys. Chem. 74, 1037 (1970).
J. Homer, M. H. Everdell, C. J. Jackson, and P. M. Whitney,J.C.S. Faraday Trans. II 68, 874 (1972).
P. Boule,J. Chem. Phys. 57, 5285 (1972).
P. Picker, P.-A. Leduc, P. R. Philip, and J. E. Desnoyers,J. Chem. Thermodyn. 3, 631 (1971).
P. Picker, E. Tremblay, and C. Jolicoeur,J. Solution Chem. 3, 377 (1974).
L. G. Hepler and D. V. Fenby,J. Chem. Thermodyn. 5, 471 (1973).
T. Matsui, L. G. Hepler, and D. V. Fenby,J. Phys. Chem. 77, 2397 (1973).
J. Gmehling, U. Onken, and W. Arlt,Vapor-Liquid Equilibrium Data Collection, Chemistry Data Series, Vol. 1, Pt. 7 (Deutsche Gesellschaft fur Chemisches Apparatewesen, 1980).
J. F. Smith and L. G. Hepler, manuscript in preparation.
I. Nagata, K. Tamura, and S. Tokuriki,Thermochim. Acta 47, 315 (1981).
R. P. Rastogi, J. Nath, and R. R. Misra,J. Chem. Thermodyn. 3, 307 (1971).
G. J. Mains, J. W. Larson, and L. G. Hepler,J. Phys. Chem. 88, 1257 (1984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grolier, JP.E., Roux-Desgranges, G., Kooner, Z.S. et al. Thermal and volumetric properties of chloroform+benzene mixtures and the ideal associated solution model of complex formation. J Solution Chem 16, 745–752 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00652577
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00652577