Conclusions
-
1.
Alloying the YuNDK15 alloy with 2% Sn, 1% In, or 0.6% Ga increases the maximum magnetic energy of the alloy by 30–40%.
-
2.
Tin, indium, and gallium increase the resistance of the β2 solid solution to high-temperature decomposition, which makes it possible to reduce the thermomagnetic treatment temperature to 900–950°C.
-
3.
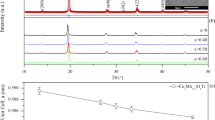
X-ray structural analysis indicates that tin, indium, and gallium enter into the composition of the β and β and β2 phases.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
A. S. Zaimovskaya, P. I. Denisov, and V. S. Vol'kshtein, Stal', No. 5 (1938).
N. G. Shul'ga, Yu. A. Skakov, and V. S. L'vov, Nauchnye Zapiski L'vovskogo Politekhnicheskogo Instituta; Seriya Mashinostroitel'naya, Issue 31, No. 7 (1955).
Ya. M. Dovgalevskii, Cast Magnets from Magnico Alloys [in Russian], Mashinostroenie, Moscow (1964).
Additional information
Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 2, pp. 16–17, February, 1969.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oblezin, A.G. The magnetic properties and structure of alloy YuNDK15 with tin, indium, and gallium. Met Sci Heat Treat 11, 98–99 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00652272
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00652272