Abstract
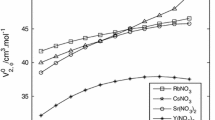
The apparent, φ v , and partial, \(\bar V_2 \) molal volumes of dilute (0.02 to 0.7m) aqueous boric acid, B(OH)3, and sodium borate, NaB(OH)4, solutions have been determined from 0 to 50° C from precision density measurements. The φ v of boric acid is a linear function of the first power of concentration. For sodium borate, the Debye-Hückel theoretical limiting law slope for the φ v as a function of the square root of molar concentration is approached at all temperatures studied. The positive deviations at higher concentrations increase with decreasing temperature. The infinite-dilution volume properties of both B(OH)3 and NaB(OH)4 indicate that these solutes behave like “structure breakers” between 0 and 50°C (that is ∂2φ ° v /∂T2 is negative). The volume change for the ionization of boric acid in water \(\Delta \bar V^\circ \), is calculated from the volume data at various temperatures. This volume change has been used to estimate the effect of pressure on the ionization of boric acid solutions from 0 to 50°C and 0 to 1000 bars. The calculated effect of pressure on the ionization is in good agreement with direct measurements.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. D. Hammann,Physico Chemical Effects of Pressure (Butterworths, London, 1957).
F. J. Millero, E. V. Hoff, and L. Kahn,J. Solution Chem. 1, 309 (1972).
E. G. Moberg, D. M. Greenberg R. Revelle, and E. C. Allen,Bull. S.I.O., Tech. Ser. 3, 231 (1934).
F. Fischer, E. Yeager, J. Miceli, and R. Bressel,J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 53, 364 (1973).
N. Ingri,Acta Chem. Scand. 11, 1034 (1957);ibid.,17, 573 (1963).
N. Ingri,Svensk. Kem. Tidsk. 75, 199 (1963).
R. F. Platford,Can J. Chem. 47, 2271 (1969).
G. S. Kell,J. Chem. Eng. Data 12, 66 (1967).
F. Vaslow,J. Phys. Chem. 73, 3745 (1969).
F. J. Millero,J. Phys. Chem. 74, 356 (1970).
A. von Endredy,Z. Anorg. Chem. 222, 285 (1935).
A. J. Ellis,Chem. Comm. 21, 802 (1966); A. J. Ellis and I. M. McFadden,Geochim. Cosmoch. Acta 36, 413 (1972).
F. J. Millero,Chem. Rev. 71, 147 (1971).
F. J. Millero, The Partial Molal Volume of Electrolytes, inStructure and Transport Processes in Water and Aqueous Solutions, R. A., Horne, ed. (Wiley and Sons, New York, 1972).
L. G. Hepler,Can. J. Chem. 47, 4613 (1969).
O. Redlich and D. Meyer,Chem. Rev. 64, 221 (1964).
J. O. Edwards, G. C. Morrison, V. F. Ross, and J. W. Schultz,J. Am. Chem. Soc. 77, 266 (1955).
I. Hansson, Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Gotenborg, Sweden (1972).
C. Culberson, M.S. Thesis, Oregon State University (1970).
A. J. Ellis and D. W. Anderson,J. Chem. Soc., 4678 (1961).
A. Disteche and S. Disteche,J. Electrochem. Soc. 114, 330 (1967).
D. A. Lown, H. R. Thirsk, and Lord Wynne-Jones,Trans. Faraday Soc. 64, 2073 (1968).
C. Culberson and R. M. Pytkowicz,Limnol. Oceanog. 13, 403 (1968).
S. D. Hamann, Com. Sci. Ind. Res. Org., Div. Appl. Chem., Tech. Paper No. 3:4 (1972).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Taken from a thesis submitted by Gary K. Ward in partial fulfillment of the requirements of the Master of Science degree, University of Miami, Miami, Florida 33149.
Scientific Contribution Number 1726 from the University of Miami, Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science, Miami, Florida 33149.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ward, G.K., Millero, F.J. The effect of pressure on the ionization of boric acid in aqueous solutions from molal-volume data. J Solution Chem 3, 417–430 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00651533
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00651533