Abstract
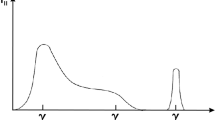
Positron-electron pair radiation is examined as a mechanism that could be responsible for the impulsive phase emission of the 5 March, 1979 transient. Synchrotron cooling and subsequent annihilation of the pairs can account for the energy spectrum, the very high brightness, and the ∼0.4 MeV feature observed from this transient, whose source is likely to be a neutron star in the supernova remnant N49 in the Large Magellanic Cloud. In this model, the observed radiation is produced in the skin layer of a hot, radiation-dominated pair atmosphere, probably confined to the vicinity of the neutron star by a strong magnetic field. The width of this layer is only about 0.1 mm. In this layer, ∼1012 generations of pairs are formed (by photon-photon collisions), cooled and annihilated during the ∼0.15 s duration of the impulsive phase. The very large burst energy implied by the distance of the LMC, and its very rapid release, are unsolved problems. We mention, nonetheless, the possibility of neutron star vibrations, which could transport the energy coherently to the surface, heat the atmosphere mechanically to a hot, pair-producing temperature, and have a characteristic damping time roughly equal to the duration of the impulsive phase.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aharonian, F. A. and Ozernoy, L. M.: 1979,Astron. Tsiz. No. 1072 p. 1.
Barat, S., Chambon, G., Hurley, K., Niel, M., Vendrenne, G., Estulin, I. V., Kurt, V. G. and Zenchenko, V. M.: 1979,Astron. Astrophys. 79, L24.
Bussard, R. W., Ramaty, R. and Drachman, R. J.: 1979,Astrophys. J. 228, 928.
Cavallo, G. and Rees, M. J.: 1978,Monthly Notices Roy. Astron. Soc. 183, 359.
Chupp, E. L., Forrest, D. J., Higbie, P. R., Suri, A. N., Tsai, C. and Dunphy, P. P.: 1973,Nature 241, 333.
Cline, T. L.: 1980,Comments on Astrophysics (in press).
Cline, T. L., Desai, U. D., Pizzichini, G., Teegarden, B. J., Evans, W. D., Klebesadel, R. W., Laros, J. G., Hurley, K., Niel, M., Vedrenne, G., Estulin, I. V., Kuznetsov, A. V., Zenchenko, V. M., Hovestadt, D. and Gloeckler, G.: 1980,Astrophys. J. 237, L1.
Detweiler, S. L.: 1975,Astrophys. J. 197, 203.
Evans, W. D., Klebesadel, R. V., Laros, J. G., Cline, T. L., Desai, U. D., Pizzichini, G., Teegarden, B. J., Hurley, K., Niel, M., Vedrenne, G., Estulin, I. V., Kuznetsov, A. V. and Zenchenko, V. M.: 1980,Astrophys. J. 237, L7.
Ginzburg, V. L. and Syrovatskii, S. I.: 1964,Origin of Cosmic Rays, Pergamon, New York.
Hartle, J. B., Sawyer, R. F. and Scalapino, D. J.: 1975,Astrophys. J. 199, 471.
Helfand, D. J. and Long, K. S.: 1979,Nature 282, 589.
Hudson, H. S., Bai, T., Gruber, D. E., Matteson, J. L., Nolan, T. L. and Peterson, L. E.: 1980,Astrophys. J. 236, L91.
Hurley, L.: 1980,COSPAR Proc. (in press).
Jacobson, A. S., Ling, J. C., Mahoney, W. A. and Willett, J. B.: 1978, in T. L. Cline and R. Ramaty (eds),Gamma Ray Spectroscopy in Astrophysics, p. 228; NASA TM 79619.
Landau, L. D. and Lifshitz, E. M.: 1958,Statistical Physics, Pergamon Press, London.
Leventhal, M., MacCallum, C. J. and Stang, P. D.: 1978,Astrophys. J. 225, L11.
Lingenfelter, R. E., Higdon, J. C. and Ramaty, R.: 1978, in T. L. Cline and R. Ramaty (eds),Gamma Ray Spectroscopy in Astrophysics, p. 252; NASA TM 79619.
Mazets, E. P. and Golenetskii, S. V.: 1979, A. F. Ioffe Physico-Technical Institute, Preprint 632.
Mazets, E. P., Golenetskii, S. V., Il'inskii, V. N., Aptekar', R. L. and Gur'yan, Yu. A.: 1979,Nature 282, 587.
Petschek, A. G. and Colvin, J. D.: 1981 (to be published).
Ramaty, R., Bonazzola, S., Cline, T. L., Kazanas, D. and Mészáros, P.: 1980,Nature 287, 122.
Ramaty, R., Kozlovsky, B. and Lingenfelter, R. E.: 1979,Astrophys. J. Suppl. 40, 487.
Ramaty, R. and Lingenfelter, R. E.: 1979,Nature 278, 127.
Ruderman, M.: 1975,Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 262, 164.
Schmidt, W. K. H.: 1978,Nature 271, 525.
Shapiro, S. L. and Salpeter, E. E.: 1975,Astrophys. J. 198, 671.
Teegarden, B. J. and Cline, T. L.: 1980,Astrophys. J. 236, L67.
Thorne, K. S.: 1969,Astrophys. J. 158, 1.
Vedrenne, G.: 1980,COSPAR Proc. (in press).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramaty, R., Lingenfelter, R.E. & Bussard, R.W. Synchrotron cooling and annihilation of ane +-e − plasma: The radiation mechanism for the 5 March, 1979 transient. Astrophys Space Sci 75, 193–203 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00651395
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00651395