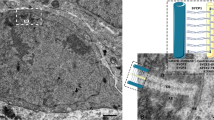
Abstract
The synaptonemal complex (SC) in the beetleBlaps cribrosa contains a highly organized central element (CE), two flanking lateral elements (LEs), and a number of regularly spaced transverse filaments (TFs) crossing the central region. The CE is built like a ladder with two longitudinal components running in parallel and a number of regularly spaced transverse CE components, briding the two longitudinal components. The CE is multi-layered with the ladders of the individual layers more or less in register. Essentially every TF originates in one of the LEs, crosses the CE through a transverse CE component and reaches the opposite LE; every transverse CE component in a given layer corresponds to one, and only one, TF. In a CE layer, short irregular pillars form the junctions between the transverse and longitudinal CE components. Adjacent pillars are connected to each other by fine fibrous bridges: the two pillars in the same transverse CE component are linked, and so are the pillars along each longitudinal component, and also more occasionally adjacent pillars in separate CE layers. It is proposed that a TF with the two associated short pillars represents the structural unit in the central region. The ordered structure of the CE is accomplished by linking adjacent pillars to each other into the well-defined three-dimensional organization of the CE.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebi U, Cohn J, Buhle L, Gerace L (1986) The nuclear lamina is a meshwork of intermediate-type filaments. Nature 323:560–564
Carpenter ATC (1975) Electron microscopy of meiosis inDrosophila melanogaster females. I: Structure, arrangement, and temporal changes of the synaptonemal complex in wild-type. Chromosoma 51:157–182
Chen QF, Pearlman RE, Moens PB (1992) Isolation and characterization of a cDNA encoding a synaptonemal complex protein. Biochem Cell Biol 70:1030–1038
Comings DE, Okada TA (1970) Whole mount electron microscopy of meiotic chromosomes and the synaptonemal complex. Chromosoma 30:269–286
Crowther RA, DeRosier DJ, Klug A (1970) The reconstruction of a three-dimensional structure from projections and its application to electron microscopy. Proc R Soc Lond A 317:319–340
Fawcett DW (1956) The fine structure of chromosomes in the meiotic prophase of vertebrate spermatocytes. J Biophys Biochem Cytol 2:403–406
Fuge H (1979) Syhapsis, desynapsis, and formation of polycomplex-like aggregates in male meiosis ofPales ferruginea (Diptera, Tipulidae). Chromosoma 70:353–373
Guénin H-A (1953) Les chromosomes sexuels multiples duBlaps polychresta Forsk. (Col. Ténébr.). Rev Suisse Zool 60:462
Guénin H-A, Gautier A (1960) Observations sur la structure submicroscopic des chromosomes duBlaps mucronata Latr. (Col. Tenebr.). Note préliminaire. Rev Suisse Zool 67:210–216
Heitlinger E, Peter M, Häner M, Lustig A, Aebi U, Niggs EA (1991) Expression of chicken lamin B2 inEscherichia coli: characterization of its structure, assembly, and molecular interactions. J Cell Biol 113:485–495
Heyting C, Dietrich AJJ, Moens PB, Dettmers RJ, Offenberg HH, Redeker EJW, Vink ACG (1989) Synaptonemal complex proteins. Genome 31:81–87
Hirokawa N, Glickman MA, Willard MB (1984) Organization of mammalian neurofilament polypeptides within the neural cytoskeleton. J Cell Biol 98:1523–1536
Mehlin H, Daneholt B, Skoglund U (1992) Translocation of a specific premessenger ribonucleoprotein particle through the nuclear pore studied with electron microscope tomography. Cell 69:605–613
Meuwissen RLJ, Offenberg HH, Dietrich AJJ, Riesewijk A, Heyting C (1992) A coiled-coil related protein specific for synapsed regions of meiotic prophase chromosomes. EMBO J 11:5091–5100
Moens PB (1968) The structure and function of the synaptonemal complex inLilium longiforium sporocytes. Chromosoma 23:418–451
Moens PB (1969a) The fine structure of meiotic chromosome polarization and pairing inLocusta migratoria spermatocytes. Chromosoma 28:1–25
Moens PB (1969b) Multiple core complexes in grasshopper spermatocytes and spermatids. J Cell Biol 40:542–551
Moses MJ (1956) Chromosomal structures in crayfish spermatocytes. J Biophys Biochem Cytol 2:215–218
Moses MJ (1968) Synaptinemal complex. Annu Rev Genet 2:363–412
Moses MJ, Dresser ME, Poorman PA (1984) Composition and role of the synaptonemal complex. In: Evans CW, Dickinson HG (eds) Controlling events in meiosis. The Company of Biologists Limited, Cambridge, UK, pp 245–270
Rasmussen SW (1976) The meiotic prophase inBombyx mori females analyzed by three-dimensional reconstructions of synaptonemal complexes. Chromosoma 54:245–293
Roth TF (1966) Changes in the synaptonemal complex during meiotic prophase in mosquito oocytes. Protoplasma (Wien) 61:346–386
Schmekel K, Skoglund U, Daneholt B (1993) The three-dimensional structure of the central region in synaptonemal complex: a comparison between rat and two insect species,Drosophila melanogaster andBlaps cribrosa. Chromosoma 102:682–692
Skoglund U, Daneholt B (1986) Emerging techniques: Electron microscope tomography. Trends Biochem Sci 11:499–503
Skogland U, Andersson K, Strandberg B, Daneholt B (1986) Three-dimensional structure of a specific premessenger RNP particle established by electron microscope tomography. Nature 319:560–564
Smith A, Benavente R (1992) Identification of a structural protein component of rat synaptonemal complexes. Exp Cell Res 198:291–297
Solari AJ, Moses MJ (1973) The structure of the central region in the synaptonemal complex of hamster and cricket spermatocytes. J Cell Biol 56:145–152
Sotelo JR, Wettstein R (1966) Fine structure of meiotic chromosomes. Comparative study of nine species of insects. Chromosoma 20:234–250
Steinert PM, Roop DR (1988) Molecular and cellular biology of intermediate filaments. Annu Rev Biochem 57:593–625
Steinert PM, Steven AC, Roop DR (1985) The molecular biology of intermediate filaments. Cell 42:411–419
Stewart M (1993) Intermediate filament structure and assembly. Curr Opin Cell Biol 5:3–11
Sym M, Engebrecht J, Roeder GS (1993) ZIP1 is a synaptonemal complex protein required for meiotic chromosome synapsis. Cell 72:365–378
von Wettstein D, Rasmussen SW, Holm PB (1984) The synaptonemal complex in genetic segregation. Annu Rev Genet 18:331–413
Wahrman J, Nezer R (1976) Disjunction and ultrastructure of a sex-chromosome complex. Chromosomes Today 5:464
Wahrman J, Nezer R, Freund O (1973) Multiple sex chromosome mechanism with “segregation bodies’. Chromosomes Today 4:434
Westergaard M, von Wettstein D (1970) Studies on the mechanism of crossing over. IV. The molecular organization of the synaptonemal complex inNeottiella (Cooke) Saccardo (Ascomycetes). CR Trav Lab Carlsberg 37:239–267
Westergaard M, von Wettstein D (1972) The synaptonemal complex. Annu Rev Genet 6:71–110
Wettstein R, Sotelo R (1971) The molecular architecture of the synaptonemal complex. Adv Cell Mol Biol 1:109–152
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by: D.P. Bazett-Jones
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmekel, K., Wahrman, J., Skoglund, U. et al. The central region of the synaptonemal complex inBlaps cribrosa studied by electron microscope tomography. Chromosoma 102, 669–681 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00650893
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00650893