Conclusions
-
1.
The importance of X-ray shadow microscopy for defining the structural condition of complex alloys after heat treatment and after longtime hot testing has been established.
-
2.
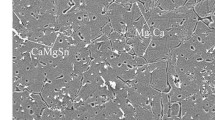
The structure of the cast alloy AL19 consists of α-solid solution depleted in copper but enriched in manganese; a CuAl2 phase which crystallizes mainly as large plates along the α-solution grains and a phase T(Al12Mn2Cu) appearing as fine particles largely distributed throughout the volume of the α-solution grains but also as relatively large platelets at grain boundaries and finally, an Al3Ti phase also of the platelet type.
-
3.
The structure of solution-treated AL19 consists of an α-solid solution enriched in copper but with reduced manganese compared with the as-cast condition and a T(Al12Mn2Cu) phase in the form of a multitude of minute particles distributed within the α-grains. The primary Al3Ti and T-phase plate-like particles remain practically unchanged.
-
4.
After long-time tests at 300°C the alloy structure consists of a non-uniform α-solid solution. A multitude of T particles exists within the grains. This structural condition is very clearly revealed by X-ray shadow microscopy.
-
5.
The complex microheterogenous structure of the α-solid solution grains in alloy AL19 with a multitude of small (several μ in size) T-phase particles apparently strongly hampers the movement of dislocations on slip planes and along boundaries thereby inproving the hot strength of the alloy.
-
6.
The low diffusivity of manganese compared with zinc, magnesium, copper, silicon and other elements and the weak tendency to coalesce of the manganese phase particles both inside the α-grains and along their boundaries slow down the softening of the alloy. This could account for the increased hot strength of AL19 compared with alloy AL7.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
I. F. Kolobnev, Casting of Aluminum Alloys (St. Fasonnoe Lit'e Alyum. Spl.) Mashgiz Press, 1953 [Book, in Russian].
I. F. Kolobnev, Collection of Papers on Light Metal Alloys, Akad. Nauk SSSR Press, 1958, #1 (Sb. Legkie Splavy) [Book in Russian].
L. P. Luzhnikov and O. A. Romanova, Collection of Papers on Light Metal Alloys, Akad. Nauk SSSR Press, 1958, #1 (Sb. Legkie Splavy) and Aluminum and Manganese Alloys (Alyum. i Magnievye Splavy) Oborongiz Press, 1959.
E. H. Dix, Canadian Aeronaut. Journal, vol 2, 1956, #1, 11–20.
P. L. Thorpe, G. R. Tremain and R. W. Ridley, Journal Inst. Metals, vol. 77, April 1950, #4, 111–140.
I. L. Rogel'berg, E. S. Shpichenetskii and V. V. Chutko, Symposium on Metal Science of Nonferrous Metals and Alloys, (Sb. Metallovedenie Tsvetn. Metal. i Spl.) Metallurgizdat, 1959.
G. Falkenhagen and W. Hofmann, Zeitschrift Metallkunde, vol. 43, 1952, #3, 69–81.
I. N. Fridlyander, Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR, vol 104, 1955, #3, 429–432.
B. M. Rovinskii and S. G. Gabashidze, Zavodskaya Laboratoriya, vol 17, 1951, #2 [Not exported. TN]
K. I. Ivanov, Zhur. Tekhn. Fiz., vol. 19, 1949, #11.
W. Betteridge and R. S. Sharpe, Journal Iron Steel Institute, vol. 158, 1948, 185–191.
B. M. Rovinskii, V. G. Lyuttsau and I. A. Avdeenko, Izv Akad. Nauk SSSR, Physical Series, vol. 20, 1957, #7.
V. G. Lyuttsau, Zavodskaya Laboratoriya, vol. 25, 1959, #3
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kolobnev, I.F., Lyut'tsau, V.G. & Aristova, N.A. Effect of manganese on the hot strength of aluminum alloys. Met Sci Heat Treat 2, 495–498 (1960). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00649728
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00649728