Abstract
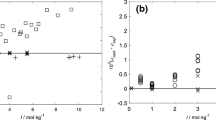
Electromotive force measurements were carried out on the HCl−ZnCl2−H2O system at constant total ionic strengths of 0.1, 0.2, 0.5, 1.0 and 2.0 mol-kg−1 at 25 and 35°C using a cell consisting of Pt, H2(g, 1 atm)|HCl(mA), ZnCl2(mB)|AgCl/Ag. The data were interpreted by the mixed electrolyte equations of Pitzer and Kim in order to evaluate mixing ion-interaction parameters. The activity coefficients of ZnCl2 and the Gibbs excess free energies of mixing are calculated and presented at I=2.0 mol-kg−1 and compared with similar systems containing transition metal chlorides.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. H. Khoo,J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 82, 1 (1986).
K. S. Pitzer,J. Phys. Chem. 77, 268 (1973).
K. S. Pitzer and G. Mayorga,J. Phys. Chem. 77, 2300 (1973).
K. S. Pitzer, and J. J. Kim,J. Am. Chem. Soc. 96, 5701 (1974).
K. S. Pitzer,J. Solution Chem. 4, 249 (1975).
C. J. Downes,J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. I 68, 1964 (1972).
K. H. Khoo, T. K. Lim, and C. Y. Chan,J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. I 74, 2037 (1978).
K. H. Khoo, T. K. Lim, and C. Y. Chan,J. Solution Chem. 7, 291 (1978).
H. A. Flasche,EDTA Titration (Pergamon, New York, 1959).
A. I. Vogal,A Test Book of Quantitative Inorganic Analysis, Theory and Practice (Langmans, Green and Co. London/New York/Toronto, 1957).
D. J. G. Ives and G. J. Janz,Reference Electrodes (Academic Press, New York, 1961), Chap. 4.
R. G. Bates,Electrometric pH Determinations (Wiley, New York; Chapman and Hall, London, 1954).
R. G. Bates, E. A. Guggenheium, H. S. Harned, D. J. G. Ives, G. J. Janz, C. B. Monk, J. E. Prue, R. A. Robinson, R. H. Stokes, and W. F. K. Wynne-Jones,J. Chem. Phys. 25, 361 (1956);26, 222 (1957).
J. Ananthaswamy and G. Atkinson,J. Chem. Eng. Data 29, 81 (1984).
R. G. Anstiss and K. S. Pitzer,J. Solution Chem. 20, 849 (1991).
R. N. Goldberg,J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data,10, 1 (1981).
H. T. Kim and W. J. Frederick, Jr.J. Chem. Eng. Data 33, 177 (1988).
J. Ananthaswamy and G. Atkinson,J. Solution Chem. 11, 509 (1982).
A. V. Usha, Krishnam Raju, and G. Atkinson,J. Phys. Chem. 91, 4796 (1987).
H. Tialowska-Mocharla and G. Atkinson,J. Phys. Chem. 89, 4884 (1984).
H. T. Kim and W. J. Frederick, Jr.,J. Chem. Eng. Data 33, 278 (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tialowska-Mocharla, H., Manohar, S. & Atkinson, G. Activity coefficient measurements of the system HCl−ZnCl2−H2O at 25 and 35°C. J Solution Chem 21, 545–555 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00649563
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00649563